This chapter also gives you a general description for accessing telnet and describes the firmware versions for the routers explained in this manual.
Note: For Windows 7 user, please make sure the Windows Features of Telnet Client has been turned on under Control Panel>>Programs.
Enter cmd and press Enter. The Telnet
terminal will be open later.
In the following window, type Telnet 192.168.1.224 as below and press Enter. Note that the IP address in the example is the default address of the router. If you have changed the default, enter the current IP address of the router.
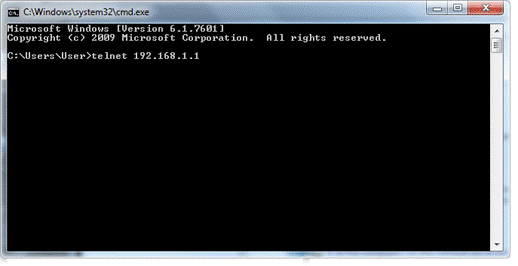
Next, enter admin/admin for Account/Password.
For users using
previous Windows system (e.g., XP), simply click Start >> Run and type Telnet 192.168.
Next, enter admin/admin for Account/Password.
Enter ? to get a list of available commands.
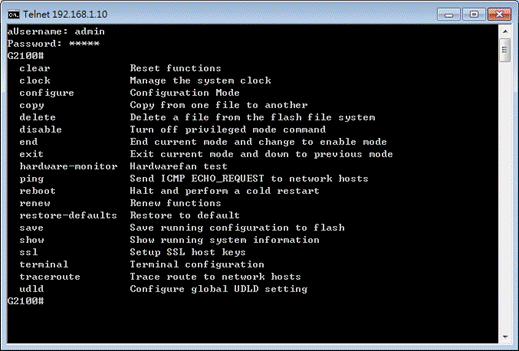
The availabe commands contain – clear, clock, configure, copy, delete, disable, end, exit, hardware-monitor, ping, reboot, renew, restore-defaults, save, show, ssl, terminal, traceroute and udld. Each command will be explained as follows.
Note: You can also enter ? to check if there are subcommands under current command.
This command allows resetting the functions of ARP, authentication, gvrp, interfaces, IP, IPv6, LACP, Line, LLDP, Logging, MAC, mvr, and Spanning Tree.
Telnet Command: clear arp
Use this command to clear entries in the ARP cache.
Syntax Items
clear arp
Description
|
Syntax Items |
Description |
|
clear arp |
<A.B.C.D>
- Enter the IP address of the device (e.g., 192.168.1.224). Related Syntax: l # clear arp l
# clear arp
<A.B.C.D> |
Example
|
G2100# clear arp 192.168.1.224 G2100# |
Telnet Command: clear authentication
Use this command to clear authentication sessions based on LAN port, MAC address, or authentication type for 802.1x/MAC authentication.
Syntax Items
clear authentication sessions
clear authentication sessions interfaces gigabitethernet
clear authentication sessions
mac
clear authentication sessions
session-id
clear authentication sessions
type
Description
|
Syntax Items |
Description |
|
clear authentication sessions |
Clear all of the sessions related to authentication. Related Syntax: l
# clear
authentication sessions |
|
clear authentication sessions interfaces gigabitethernet |
Clear the sessions of a specific interface. <1-10> - Enter the number of LAN port. Related Syntax: l
# clear
authentication sessions interfaces gigabitethernet <1-10> |
|
clear authentication sessions mac |
Clear the sessions with the
MAC address set here. <A:B:C:D:E:F> - Enter the MAC address of the device that you want to
clear the authentication information. Related Syntax: l
# clear
authentication sessions mac <A:B:C:D:E:F> |
|
clear authentication sessions session-id |
Clear the sessions with the string set here. <WORD> - Enter a string of a session that you
want to clear. Related Syntax: l
# clear
authentication sessions session-id <WORD> |
|
clear authentication sessions type |
Clear the sessions with authentication type selected
here. <dot1x> - Use 802.1x
authentication. <mac> - Use mac-based
authentication. <web> - Use web-based
authentication. Related Syntax: l
# clear
authentication sessions type <dot1x><mac><web> |
Example
|
G2100#
clear authentication sessions No
Auth Manager sessions currently exist G2100#
clear authentication sessions mac 48:5B:39: G2100#
clear authentication sessions interfaces GigabitEthernet 2 G2100#
clear authentication sessions session-id 0000000B002AFBE8 |
Telnet Command: clear gvrp
Use this command to clear statistics or port error statistics for all interfaces or a specific interface (LAN or LAG).
Syntax Items
clear gvrp error-statistics
clear gvrp statistics
Description
|
Syntax Items |
Description |
|
clear gvrp error-statistics |
Specify a LAN/LAG interface for clearing error
statistics for GVRP. <1 - 10> - Enter the number (1 to 10) of LAN port. <1 - 8> - Enter the number (1 to 8) of LAG interface (IEEE
802.3 Link Aggregation Interface) that you want to clear the GVRP setting. Related Syntax: l # clear gvrp error-statistics interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-10> l
# clear gvrp error-statistics
interfaces LAG <1-
8> |
|
clear gvrp statistics |
Specify a LAN/LAG interface for clearing statistics
for GVRP. <1 - 10> - Specify an interface for clearing statistics for
GVRP. <1 - 8> - Specify LAG interface for clearing statistics for
GVRP. Related Syntax: l # clear statistics interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-10> l
# clear statistics interfaces LAG
<1- 8> |
Example
|
G2100# clear gvrp error-statistics interfaces
GigabitEthernet 2 G2100# G2100# clear gvrp error-statistics interfaces LAG 2 G2100# |
Telnet Command: clear interfaces
Use this command to clear
statistics counters for all interfaces or a specific interface (LAN or LAG).
Syntax Items
clear interfaces GigabitEthernet
clear interfaces LAG
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
clear interfaces GigabitEthernet |
Specify a LAN/LAG interface for clearing
statistics counters on that port. <1-10> - Enter the number (1 to 10) of LAN
port. Related Syntax: l
# clear interfaces gigabitEthernet <1-10>
counters |
|
clear interfaces LAG |
Specify a LAG interface for clearing
statistics counters on that port. <1 - 8> -
Enter the number
(1 to 8) of LAG interface (IEEE 802.3 Link Aggregation Interface). Related Syntax: l
# clear interfaces LAG <1 -
8> counters |
Example
|
G2100# clear interfaces gigabitethernet 3
counters G2100# clear interfaces G2100# clear interfaces lag 2 counters G2100# |
Telnet Command: clear ip
Use this command to clear ARP
inspection information, DHCP snooping database agent, and IGMP snooping groups
(dynamic or static) information for all interfaces or a specific interface (LAN
or LAG) with IP address.
Syntax Items
clear ip arp
clear ip dhcp
clear ip igmp
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
clear ip igmp |
snooping groups
dynamic -
Clear dynamic snooping groups of IGMP server. snooping groups
static - Clear
static snooping groups of IGMP server. snooping
statistics - Clear
snooping statistics for IGMP server. Related Syntax: l # clear ip igmp snooping groups dynamic l # clear ip igmp snooping groups static l
# clear ip
igmp snooping statistics |
|
clear ip dhcp |
snooping
database statistics -
Clear snooping database statistics for DHCP server. snooping
interfaces GigabitEthernet / LAG-
Specify a LAN / LAG interface for clearing DHCP snooping information. <1 - 10> - Enter the number (1 to 10) of LAN
port. <1 - 8> -
Specify a LAG
interface for clearing DHCP snooping information. Related Syntax: l # clear ip dhcp snooping database statistics l # clear ip dhcp snooping interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-10> statistics l
# clear ip dhcp snooping interfaces LAG <1- 8> statistics |
|
clear ip igmp |
snooping groups
dynamic -
Clear dynamic snooping groups of IGMP server. snooping groups
static - Clear
static snooping groups of IGMP server. snooping statistics
- Clear snooping
statistics for IGMP server. Related Syntax: l # clear ip igmp snooping groups dynamic l # clear ip igmp snooping groups static l
# clear ip
igmp snooping statistics |
Example
|
G2100# clear
ip igmp snooping groups dynamic G2100# |
Telnet Command: clear ipv6
Use this command to clear MLD snooping configuration for dynamic / static
group(s) with IPv6 address.
Syntax Items
clear ipv6 mld
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
clear ipv6 mld |
snooping groups
dynamic -
Clear dynamic snooping groups of MLD. snooping groups
static - Clear
static snooping groups of MLD. Related Syntax: l # clear ipv6 mld snooping groups dynamic l
# clear ipv6
mld snooping groups static |
Example
|
G2100# clear ipv6 G2100# clear ipv6 mld snooping groups
dynamic G2100# clear ipv6 mld snooping groups
dynamic?
<cr> G2100# clear ipv6 mld snooping groups
static |
Telnet Command: clear lacp
Use this command to clear LACP configuration for specified LAG interface
or all LAG intefaces.
Syntax Items
clear lacp <1-8> counters
clear lacp counters
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
clear lacp <1-8> |
<1-8> - Enter the number (1 to 8) of LAG
interface (IEEE 802.3 Link Aggregation Interface). Related Syntax: l
# clear lacp <1-8> counters |
|
clear lacp counters |
Clear LACP
configuration for all LAG interfaces. Related Syntax: l
# clear lacp counters |
Example
|
G2100# clear lacp 1 counters No interfaces configured in the channel
group G2100# |
Telnet Command: clear line
Use this command to clear line
settings including SSH (Secure Shell) configuration and telnet daemon
configuration.
Syntax Items
clear line ssh
clear line telnet
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
clear
line ssh |
Clear SSH configuration for line
connection. Related Syntax: l
# clear line ssh |
|
slear
line telnet |
Clear SSH Telnet configuration for line
connection. Related Syntax: l
# clear line telnet |
Example
|
G2100# clear line ssh G2100# clear line telnet |
Telnet Command: clear lldp
Use this command to clear LLDP statistics or reset LLDP information.
Syntax Items
clear lldp global
clear lldp interfaces
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
clear lldp global |
Clear all of the statistics related to
LLDP. Related Syntax: l
# clear lldp global statistics |
|
clear lldp interfaces |
Specify a LAN / LAG interface for
clearing LLDP information. <1-10> - Enter the number (1 to 10) of LAN
port. <1-8> - Enter the number (1 to 8) of LAG
interface (IEEE 802.3 Link Aggregation Interface). Related Syntax: l # clear lldp interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-10> statistics l
# clear lldp interfaces LAG
<1-8> statistics |
Example
|
G2100# clear lldp global statistics G2100# G2100# clear lldp interfaces LAG 1
statistics G2100# clear lldp interfaces
gigabitethernet 1 statistics G2100# |
Telnet Command: clear logging
Use this command to clear log
messages from the internal logging buffer and flash.
Syntax Items
clear logging buffered
clear logging file
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
clear logging buffered |
Clear the log
stored in RAM. Related Syntax: l
# clear logging buffered |
|
clear logging file |
Clear the log
stored in flash. Related Syntax: l
# clear logging file |
Example
|
G2100# clear logging buffered G2100# clear logging file G2100# |
Telnet Command: clear mac
Use this command to clear MAC
configuration related to VLAN, LAG, and LAN port.
Syntax Items
clear mac
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
clear
mac address-table |
<1-10> - Enter the number (1 to 10) of LAN port. <1-8>- Enter the number (1 to 8) of LAG
interface (IEEE 802.3 Link Aggregation Interface). <1-4094>
- Specify a VLAN ID
by entering its number. Related Syntax: l # clear mac adderss-table dynamic interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-10> l # clear mac adderss-table dynamic interfaces LAG <1-8> l
# clear mac adderss-table dynamic vlan
<1-4094> |
Example
|
G2100# clear mac address-table dynamic
vlan 2038 G2100# clear mac address-table dynamic
interfaces gigabitethernet 3 G2100# |
Telnet Command: clear mvr
Use this command to clear
information for all members (including dynamic, static) of MVR.
Syntax Items
clear mvr members
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
clear mvr members |
Clear information for
dynamic / static members. Related Syntax: l # clear mvr members dynamic l
# clear mvr members static |
Example
|
G2100#
clear mvr members dynamic G2100#
clear mvr members static G2100# |
Telnet Command: clear spanning-tree
Use this command to clear running
system information.
Syntax Items
clear spanning-tree
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
clear spanning-tree interfaces |
Specify a LAN interface for clearing its
running information. <1-10>- Enter the number (1 to 10) of LAN
port. <1-8>- Enter the number (1 to 8) of LAG
interface (IEEE 802.3 Link Aggregation Interface). Related Syntax: l # clear spanning-tree interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> statistics l
# clear spanning-tree interfaces LAG
<1-8> statistics |
Example
|
G2100# clear spanning-tree interfaces
gigabitethernet 3 statistics G2100# clear spanning-tree interfaces LAG
1 statistics G2100# |
This command allows managing the system clock.
Telnet Command: clock set
Use this command to configure the system clock manually.
Syntax Items
clock set
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
clock set |
Set current by entering hours, minutes,
seconds, month, date and year with the format listed below: <HH:MM:SS> - Hour, minute, second
(e.g., 08:10:30). <Jan> - January. <feb> - February <mar> - March <apr> - April <may> - May <jun> - June <jul> - July <aug> - August <sep> - September <oct> - October <nov> - November <dec> - December <1-31> - Date 1 to 31. <2000-2035> - Year of 2000 to 2035. Related Syntax: l
# clock set HH:MM:SS
jan/feb/mar/apr/may/jun/jul/aug/sep/oct/nov/dec <1-31>
<2000-2035> |
Example
|
G2100# clock set 12:10:30 jan 1 2019 2019-01-01 12:10:30 UTC+8 |
This command allows configuring the settings related to VigorSwitch.
Available sub-commands under
Configure include:
aaa, acct, authentication, clock, custom, dos, dot1x, do, dray_surveillence,
enable, end, errdisable, exit, gvrp, hostname, interface, ip, ipv6, jumbo-frame,
lacp, lag, line, lldp, logging, logmail, loop-protection, mac, mailalert, management,
management-vlan, mirror, mvr, no, openvpn, poe, port-security, qos, radius, schedule,
snmp, sntp, spanning-tree, start-up, storm-control, surveillance-vlan, system,
tacacs, tr069, udld, username, vlan, voice-vlan, webhook
Before
configuration, you have to enter “configure” to access into next phase.
To return to previous phase, enter “exit”
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# exit G2100# |
Telnet Command: aaa
Use this command to add a login
authentication list to authenticate with local, tacacs+, radius, and none
service.
Syntax Items
aaa authentication enable
aaa authentication login
Description
|
Syntax Items |
Description |
|
aaa authentication enable |
Enable authentication is used only on CLI for a user trying
to switch from User EXEC (>) mode to Privileged EXEC (#) mode. enable – Enable the authentication list. <LISTNAME> – Enter a string as the list name
for authentication type. Default value is “default”. <none, enable, tacacs+,
radius> – Specify the authentication
method by entering none, enable, tacacs+ or radius. l None: Do nothing and just make user be authenticated. l Enable: Use local password to authenticate. l Tacacs+: Use remote Tacas+ server to authenticate. l Radius: Use remote Radius server to authenticate. default - It is used to configure default enable
authentication. Related Syntax: l <config>#aaa authentication enable <LISTNAME> <none, enable, tacacs+, radius> l
<config>#aaa authentication
enable default <none, enable, tacacs+, radius> |
|
aaa authentication login |
Login authentication is used when a user tries to login into the switch. <LISTNAME> – Enter a string as the list name for authentication type. Default value is “default”. <none, enable, tacacs+, radius> –Specify the authentication method by entering none, enable, tacacs+ or radius. default - It is used to configure default login authentication. Related Syntax: l <config>#aaa authentication login <none, enable, tacacs+, radius> l
<config>#aaa authentication
login default <none, enable, tacacs+, radius> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# aaa authentication enable LISTNAME enable G2100(config)# G2100(config)# exit G2100# show aaa authentication enable lists Enable List Name Authentication Method List ------------------ -------------------------------
default enable
LISTNAME enable G2100# |
Telnet Command: acct
Use this command to set RADIUS /
TACACS server.
Syntax Items
acct server radius
acct server tacacs
Description
|
Syntax Items |
Description |
|
server radius |
<1-65535> - Set a value to wait for a packet retransmission to the authentication server. <1-60> - Set the transmission interval (unit is second). l # acct server radius disconnect message port <1-65535> interval <1-60> |
|
server tacacs |
<1-65535> - Set a value to wait for a packet retransmission to the authentication server. <1-60> - Set the transmission interval (unit is second). l # acct server tacacs disconnect message port <1-65535> interval <1-60> |
Telnet Command: authentication
Use this command to enable the
global setting of 802.1x/MAC/WEB authentication network access control (default
is disabled for all).
Syntax Items
authentication dot1x
authentication guest-vlan
authentication mac
authentication web
Description
|
Syntax Items |
Description |
|
authentication dot1x |
Enable 802.1x
authentication by entering the word, dot1x after authentication. Related Syntax: l
<config># authentication dot1x |
|
authentication guest-vlan |
Configure the guest VLAN. <1-4094> - Specify a guest VLAN ID by entering its number. Related Syntax: l
<config># authentication
guest-vlan <1-4094> |
|
authentication mac |
Enable MAC authentication
by entering the word, mac after authentication. mac local - Local database for MAC-Based authentication. It can
add local MAC authentication hosts in database. <A:B:C:D:E:F> - Enter the MAC address to be added
for authentication. control auth – Set a local
entry control mode, auth (the host will be set to authorized) or unauth (the
host will be set to unauthorized). vlan <1~4094> - Specify a VLAN ID by entering its number reauth-period
<300~4294967294> - Set a time to initiate automatic re-authentication. inactive-timeout
<60~65535>- Set the inactive timeout for MAC authentication host. After
the time interval, if there is no activity from the client, then it will be
unauthorized by Vigor system. control unauth
- Set a local entry control mode as “unauth” to let the host set as
unauthorized. radius mac-case <lower / upper> - Set RADIUS
user ID with lower case or upper case. radius mac-delimiter <colon/dot/hyphen/none> -
Select RADIUS user ID delimiter. In which, colon: XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX dot: XX.XX.XX.XX.XX.XX hyphen: XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX none: XXXXXXXXXXXX gap < Related Syntax: l <config>#authentication mac l <config>#authentication mac local <A:B:C:D:E:F> control auth inactive-timeout <60~65535> l <config>#authentication mac local <A:B:C:D:E:F> control auth reauth-period <300~4294967294> l <config>#authentication mac local <A:B:C:D:E:F> control auth vlan <1~4094> l <config>#authentication mac local <A:B:C:D:E:F> control auth vlan<1~4094> reauth-period <300~4294967294> l <config>#authentication mac local <A:B:C:D:E:F> control auth vlan<1~4094> reauth-period <300~4294967294> inactive-timeout <60~65535> l <config>#authentication mac local <A:B:C:D:E:F> control unauth l <config>#authentication mac radius mac-case <lower / upper> l <config>#authentication mac radius mac-delimiter <colon/dot/hyphen/none> l
<config>#authentication mac
radius mac-delimiter <colon/dot/hyphen/none> gap < |
|
authentication web |
Web - Enable web authentication by entering the word “web” after
“authentication”. username <WORD> - Specify a username. password <string> - Set a password. vlan <1~4094> - Specify a VLAN ID by entering its number. reauth-period
<30~4294967294> - Set a time to initiate automatic re-authentication. inactive-timeout
<60~65535>- Set the inactive timeout for MAC authentication host. After
the time interval, if there is no activity from the client, then it will be
unauthorized by Vigor system. Related Syntax: l <config>#authentication web l <config>#authentication web local username <WORD> password <string> inactive-timeout <60~65535> l <config>#authentication web local username <WORD> password <string> reauth-period <300~4294967294> l <config>#authentication web local username <WORD> password <string> reauth-period <300~4294967294> inactive-timeout <60~65535> l <config>#authentication web local username <WORD> password <string> vlan<1~4094> l
<config>#authentication web
local username <WORD> password <string> vlan<1~4094>
reauth-period <30~4294967294> inactive-timeout <60~65535> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# authentication dot1x G2100(config)# vlan 3 G2100(config-vlan)# exit G2100(config)# authentication guest-vlan 3 G2100(config)# G2100(config)# exit G2100# show authentication Autentication dot1x state : enabled Autentication mac state : disabled Autentication web state : disabled Guest VLAN
: enabled (3) Mac-auth Radius User ID Format :
XXXXXXXXXXXX Mac-auth Local Entry
: Web-auth Local Entry
: Interface Configurations Interface GigabitEthernet1 Admin Control
: disable Host Mode
:
multi-auth Type web State
: disabled Type Order
: dot1x MAC/WEB Method Order : radius Guest VLAN
:
disabled Reauthentication : disabled Max Hosts
: 256 VLAN Assign Mode : static --More— ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. G2100# configure G2100(config)# authentication mac local
00:11:22:33:00:01 control auth vlan 3 reauth-period 500 inactive-timeout 300 G2100(config)# G2100(config)# authentication mac local 00:11:22:33:00:01 control unauth G2100(config)# G2100(config)# authentication web local username user_1 password
1234tw vlan 3 reauth-period 600 inactive-timeout 700 G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: clock
Use this command to configure time
zone, summer-time and external time source for the system clock.
Syntax Items
clock auto timezone
clock source local
clock source sntp
clock summer-time
clock timezone
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
clock auto timezone |
VigorSwitch sets the time zone automatically. |
|
clock source local |
Configure an
external time source for the system clock. “local” means
to use static time. It is the default setting. Related
Syntax: l
<config># clock source
local |
|
clock source sntp |
Configure an
external time source for the system clock. “sntp” means to use SNTP time. Related
Syntax: l
<config># clock source
sntp |
|
clock summer-time |
Configure the system to automatically
switch to summer time (daylight saving time). ACRONYM – Specify the acronym name of time zone.
The acronym of the time zone will be displayed when summer time is in effect.
If unspecified, the time zone acronym will be used in default. (1-4 chars) <jan/feb/mar/apr/may/jun/jul/aug/sep/oct/nov/dec>
- Indicate January,
February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October,
November, December. <1-31> means date 1 to 31. <2000-2037> - means year of 2000 to
2035. <HH:MM> - means hours and minutes. recurring - Summer time should start and
end on the corresponding specified days every year. <1-1440>- Set the number of minutes
to add during the summer time. The default number is 60. eu - The summer time is based on the
European Union rules. (Start point – last Sunday in March, End point – last
Sunday in October) first - The first week of the month. last - The last week of the month. <sun/mon/tue/wed/thu/fri/sat> - Indicate Sunday, Monday, Tuesday,
Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday. <jan/feb/mar/apr/may/jun/jul/aug/sep/oct/nov/dec>
- Indicate January,
February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October,
November, December. <first/last>- Specify the first
week or the last week of the month. <1-5> - Specify the number of the
week in the month. Note that the first group of month, date,
hour and minute is used for configuring starting time, and the second group
is used for configuring ending time. Related
Syntax: l <config># clock summer-time ACRONYM date <jan/feb/mar/apr/may/jun/jul/aug/sep/oct/nov/dec> <1-31> <2000-2037> <HH:MM> <jan/feb/mar/apr/may/jun/jul/aug/sep/oct/nov/dec><1-31><2000-2037> <HH:MM> l <config># clock summer-time ACRONYM recurring eu <1-1440> l
<config># clock summer-time
ACRONYM recurring l <config># clock summer-time ACRONYM recurring first <sun/mon/tue/wed/thu/fri/sat>< jan / feb / mar / apr / may / jun/jul/aug/sep/oct/nov/dec> <HH:MM> <first/last> <sun/mon/tue/wed/thu/fri/sat>< jan /feb /mar /apr/may/ jun/jul/aug/sep/oct/nov/dec> <HH:MM> <1-14400> l <config># clock summer-time ACRONYM recurring last <sun/mon/tue/wed/thu/fri/sat>< jan /feb /mar /apr /may /jun/jul/aug/sep/oct/nov/dec> <HH:MM> <first/last><sun/mon/tue/wed/thu/fri/sat>< jan /feb /mar /apr/may/ jun/jul/aug/sep/oct/nov/dec> <HH:MM> <1-14400> l
<config># clock summer-time
ACRONYM recurring <1-5> <sun/mon/tue/wed/thu/fri/sat>< jan
/feb /mar /apr /may /jun/jul/aug/sep/oct/nov/dec> <HH:MM>
<1-5> <sun/mon/tue/wed/thu/fri/sat>< jan /feb /mar /apr
/may/jun/jul/aug/sep/oct/nov/dec> <HH:MM> <1-14400> |
|
clock timezone ACRONYM <-12-13> minutes
<0-59> |
Set the time zone for display purposes. ACRONYM – Specify the acronym name of time zone.
The acronym of the time zone will be displayed when summer time is in effect.
If unspecified, the time zone acronym will be used in default. (1-4 chars) <-12-13>
– Specify the hour offset (from -12 to +13) of time zone. minutes
<0-59> – Specify the minute difference from UTC. Related
Syntax: l
<config># clock timezone ACRONYM
<-12-13> minutes <0-59> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# clock source sntp G2100(config)# exit G2100# show clock detail 2019-01-05 06:51:23 UTC+8 Time source is sntp Time zone: Acronym is Offset is UTC+8 G2100# configure G2100(config)# clock summer-time tw date jan 30 2019
23:30 feb 1 2019 20:50 G2100(config)# exit G2100# show clock
detail 2019-01-05 07:13:49 UTC+8 Time source is sntp Time zone: Acronym is ACRONYM Offset is UTC-10:08 Summertime: Acronym is tw Starting and ending on a specific date. Begins at 1 30 19 23:30 Ends at 2 1 19 20:50 Offset is 60 minutes. G2100# configure G2100(config)# clock summer-time ACRONYM recurring eu
1200 G2100(config)# clock summer-time ACRONYM recurring
first mon jan 10:10 first sun feb 10:10 1000 G2100(config)# exit G2100# show clock detail 2019-01-05 11:37:18 UTC+8 Time source is sntp Time zone: Acronym is Offset is UTC+8 Summertime: Acronym is ACRONYM Recurring every year. Begins at 1 1 1 10:10 Ends at 1 0 2 10:10 Offset is 1000 minutes. |
Telnet Command: custom
Use this command to enable the
module settings.
Syntax Items
custom enable
Description
|
Syntax Items |
Description |
|
custom enable |
Enable the module settings. Related Syntax: l
<config># custom enable |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# custom enable G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: dos
Use this command to enable
specific Denial of Service (DoS) protection.
Syntax Items
dos daeqsa-deny
dos icmp-frag-pkts-deny
dos icmp-ping-max-length
dos icmpv4-ping-max-check
dos icmpv6-ping-max-check
dos ipv6-min-frag-size-check
dos ipv6-min-frag-size-length
dos land-deny
dos nullscan-deny
dos pod-deny
dos smurf-deny
dos smurf-netmask
dos syn-sportl1024-deny
dos synfin-deny
dos synrst-deny
dos tcp-frag-off-min-check
dos tcpblat-deny
dos tcphdr-min-check
dos tcphdr-min-length
dos udpblat-deny
dos xma-deny
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
dos
daeqsa-deny |
Drop the packets if the destination MAC
address equals to the source MAC address. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos daeqsa-deny |
|
dos icmp-frag-pkts-deny |
Drop the fragmented ICMP packets. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos icmp-frag-pkts-deny |
|
dos
icmp-ping-max-length |
Set the maximum packet size for
ICMPv4/ICMPv6 ping operation. <0-65535> - Specify a packet number. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos icmp-ping-max-length
<0-65535> |
|
dos
icmpv4-ping-max-check |
Check ICMPv4 ping maximum packets size
and drop the packets larger than the maximum packet size defined by the
command, dos icmp-ping-max-length. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos icmpv4-ping-max-check |
|
dos
icmpv6-ping-max-check |
Check ICMPv6 ping maximum packets size
and drop the packets larger than the maximum packet size defined by the
command, icmp-ping-max-length. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos
icmpv6-ping-max-check |
|
dos ipv6-min-frag-size-check |
Check minimum size of IPv6 fragments. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos ipv6-min-frag-size-check |
|
dos
ipv6-min-frag-size-length <0-65535> |
Set the minimum packet size of IPv6
fragmented packets. <0-65535> - Specify a packet number. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos
ipv6-min-frag-size-length <0-65535> |
|
dos
land-deny |
Drop the packets if the source IP address
equals to destination IP address. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos land-deny |
|
dos
nullscan-deny |
Drop the packets if attacked by NULL
Scan. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos nullscan-deny |
|
dos
pod-deny |
Drop the packets if attacked by Ping of
Death. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos pod-deny |
|
dos
smurf-deny |
Drop the packets if encountered Smurf
attack. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos smurf-deny |
|
dos smurf-netmask |
Set the smurf attack size. <0-32> - Enter a number as smurf
attacks size. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos smurf-netmask <0-32> |
|
dos syn-sportl1024-deny |
Drop SYN packets with sport less than
1024. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos syn-sportl1024-deny |
|
dos synfin-deny |
Drop the packets with SYN and FIN bits
set. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos synfin-deny |
|
dos
synrst-deny |
Drop the packets with SYNC and RST bits
set. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos synrst-deny |
|
dos
tcp-frag-off-min-check |
Drop the TCP fragmented packet with
offset equals to the minimum packet size. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos tcp-frag-off-min-check |
|
dos tcpblat-deny |
Drop the packets if the source TCP port
equals to destination TCP port. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos tcpblat-deny |
|
dos
tcphdr-min-check |
Check the minimum TCP header and drop the
TCP packets with the header smaller than the minimum size defined. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos tcphdr-min-check |
|
dos
tcphdr-min-length |
Set the minimum size of TCP header. <0-65535> - Specify a packet number. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos tcphdr-min-length
<0-65535> |
|
dos
udpblat-deny |
Drop the packets if the source UDP port
equals to destination UDP port. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos udpblat-deny |
|
dos
xma-deny |
Drop the packets if the sequence number
is zero and the FIN, URG and PSH bits are set already. Related
Syntax: l
<config># dos xma-deny |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# dos icmp-ping-max-length 25252 G2100(config)# dos icmpv4-ping-max-check G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: dot1x
Use this command to set 802.1x configuration.
Syntax Items
dot1x guest-vlan
Description
|
Syntax Items |
Description |
|
dot1x guest-vlan |
<0-4094> - Enter a number as guest VLAN ID. Related Syntax: l <config># dot1x guest-vlan <0-4094> |
Example
|
G2100(config)#
dot1x guest-vlan 33 G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: do
Use this command to execute a
command immediately.
Syntax Items
do SEQUENCE
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
SEQUENCE |
Enter the command that you want to
execute immediately. Related
Syntax: (for example) l
<config># do show info |
Example
|
G2100(config)#
do show info System
Name : G2100 System
Location : Default System
Contact : Default MAC
Address : 14:49:BC:41:33:F4 IP
Address
: 192.168.1.11 Subnet
Mask : 255.255.255.0 Loader
Version : Loader
Date : Aug 30 2019 - 13:58:32 Firmware
Version : Firmware
Date : Nov 28 2019 - 17:06:13 Firmware
Revision : 1688 System
Object ID : System
Up Time : 3 days, 22 hours, 13 mins, 25 secs G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: dray_surveillence
Use this command to enable /
disable the ONVIF.
Syntax Items
dray_surveillence add
dray_surveillence direct-add
dray_surveillence set
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
dray_surveillence add |
Add an IP device for surveillance. WORD <36-36> - Enter the UUID string of the IP camera or IP-based device. Related Syntax: l <config># dray_surveillence add device uuid WORD <36-36> l <config># dray_surveillence add group uuid WORD <36-36> |
|
dray_surveillence direct-add |
WORD <36-36> - Enter the UUID string of the IP camera or IP-based device. Related Syntax: l <config># dray_surveillence direct-add device uuid WORD <36-36> |
|
dray_surveillence set |
WORD <36-36> - Enter the UUID string of the IP camera or IP-based device. Related Syntax: l <config># dray_surveillence set device uuid WORD <36-36> l <config># dray_surveillence set group uuid WORD <36-36> |
Example
|
G2100#
configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)#
dray_surveillence G2100(config)# G2100(config)#
dray_surveillence add device uuid
53d G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: enable
Use this command to configure
local password with encrypted string or not.
Syntax Items
enable password
enable privilege
enable secret
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
enable password |
<PASSWORD> - Edit
the password for each privilege level for activating authentication. Related
Syntax: l
<config># enable password PASSWORD
|
|
enable privilege |
Edit the privilege level of the password
for local user. <1-15> - Enter a number for
specifying a privilege level. Default value is 15. <string> - Enter a new string as
the password. Related
Syntax: l
<config>#
enable privilege <1-15> password <string> l
<config>#
enable privilege <1-15> secret <string> l
<config># enable privilege
<1-15> secret encrypted <string> |
|
enable secret |
<PASSWORD> - Enter a new string as
the encrypted password. Related
Syntax: l <config># enable secret PASSWORD l
<config># enable secret encrypted
PASSWORD |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# enable secret encrypted testtest G2100(config)# exit G2100# show running-config G2100# … enable privilege 2 secret
"OTE5ZTY4MmNhYzgyNWQ0MzBhNTgwZTg0MmZmMGJiYzQ=" enable secret "testtest" vlan 2 name
"test0002" vlan 3 name
"test0003" vlan 5 name
"test_carrie" voice-vlan oui-table 00:E0:BB "3COM" voice-vlan oui-table 00:03:6B "Cisco" voice-vlan oui-table 00:E0:75 "Veritel" ....... |
Telnet Command: end
Use this command to end current mode.
Syntax Items
end
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)#end G2100# |
Telnet Command: errdisable
Use this command to enable the
auto recovery timer for port error.
Syntax Items
errdisable recovery cause
errdisable recovery interval
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
errdisable
recovery cause |
Enable the auto recovery timer for port error disabled from
ACL,all, ARP rate limit, STP BPDU guard, broadcast flooding, DHCP rate limit, port security, STP self-loop, unicast flooding,
or unknown multicast flooding causes. Related
Syntax: l
<config># erridisable recovery
cause < acl /all /arp-inspection /bpduguard /broadcast-flood
/dhcp-rate-limit /psecure-violation /selfloop /unicast-flood
/unknown-multicast-flood > |
|
errdisable
recovery interval |
Set the recovery time of the error
disabled port. <30-86400>
- The default value is 300 seconds. Related
Syntax: l
<config># errdisable recovery
interval <30-86400> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# errdisable recovery interval 600 G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: exit
Use this command to exit current
mode and return to previous mode/phase.
Syntax Items
exit
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# exit G2100# |
Telnet Command: gvrp
Use this command to enable the
GVRP configuration. In default, the GVRP is disabled.
Syntax Items
gvrp
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# gvrp G2100(config)# G2100(config)# exit G2100# show gvrp
GVRP Status
--------------------
GVRP
: Enabled Join time
: 200 ms
Leave time
: 600 ms
LeaveAll time
: 10000 ms G2100# |
Telnet Command: hostname
Use this command to modify the
network name of VigorSwitch.
Syntax Items
hostname
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
hostname |
<word> - Enter a string as the
network name for VigorSwitch. Related
Syntax: l
<config># hostname <word> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# hostname Switch_ Switch_ |
Telnet Command: interface
Use this command to configure
interface settings.
Before configuring, you have to access into next phase. See the following example:
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# interface GigabitEthernet
3 G2280(config-if)# |
Or
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# interface range LAG 3 G2100(config-if-range)# |
Syntax Items
interface GigabitEthernet
interface VLAN
interface LAG
interface range
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
interface GigabitEthernet |
<1-10> - Specify the number of Ethernet LAN port. Related Syntax: l <config># interface GigabitEthernet <1-10> |
|
interface LAG |
<1-8> - Specify the number of LAG interface. Related Syntax: l <config># interface LAG <1-8> |
|
Interface
range |
Specify an interface ranges for configuring detailed settings. Related Syntax: l <config># interface range GigabitEthernet <1-10>
<config># interface range LAG <1-8> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# interface LAG 1 G2280(config-if)# |
Under (config-if)#, available
sub-commands are:
<config-if># authentication
<config-if># back-pressure
<config-if># custom
<config-if># description
<config-if># device-check
<config-if># dos
<config-if># dot1x
<config-if># do
<config-if># dray_surveillence
<config-if># duplex
<config-if># eee
<config-if># end
<config-if># exit
<config-if># flowcontrol
<config-if># gvrp
<config-if># ip
<config-if># ipv6
<config-if># lacp
<config-if># lag
<config-if># lldp
<config-if># loop-protection
<config-if># mac
<config-if># mvr
<config-if># no
<config-if># poe
<config-if># port-security
<config-if># power
<config-if># protected
<config-if># qos
<config-if># rate-limit
<config-if># shutdown
<config-if># spanning-tree
<config-if># speed
<config-if># storm-control
<config-if># surveillance-vlan
<config-if># switchport
<config-if># udld
<config-if># vlan
<config-if># voice-vlan
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
authentication
|
Apply Auth Manager Port Configuration
Commands to the specified interface (Ethernet port/LAG port). dot1x – Execute the 802.1x
authentication. guest-vlan – Authenticate the guest VLAN
configuration. host-mode
<multi-auth / multi-host / single-host> - Set the host mode for
authentication on this port. max-hosts
<1-256> - Set the maximum number of authenticated hoss allowed on this
port. method
<local/radius> - Set authentication method by using local or RADIUS
server. order
<dot1x / mac /web> - Add an authentication type to the order list. port-control
<auto / force-auth / force-unauth> - Set the port state of this port as
AUTO, Authorized or Unauthorized. radius-attributes
vlan reject – If the Radius server authorizes the supplicant, but does not
provide a supplicant VLAN, the supplicant will be rejected. If the parameter
is omitted, the option is applied by default. radius-attributes
vlan static - If the Radius server authorizes the supplicant but does not
provide asupplicant VLAN, the supplicant will be accepted. reauth
– Enable/Disabel Reauthentication for this port timer
<inactive> <60-65535> – Set the time value for authentication.
After the time interval, if there is no activity from the client, it will be
unauthorized. timer
quiet <0-65535> - Set the time value to wait failed authentication
exchange. timer
reauth <300-4294967294> - Set the time value. After the time interval,
an automatic re-authentication should be initiated. web –
Execute the web-based authentication. web
max-login-attempts <3-10> – Set a maximum number of login attemps on
the port. web
max-login-attempts infinite – No limit for login attempts. Related
Syntax: l <config-if># authentication dot1x l <config-if># authentication guest-vlan l <config-if># authentication host-mode <multi-auth / multi-host / single-host> l <config-if># authentication mac l <config-if># authentication max-hosts <1-256> l <config-if># authentication method <local/radius> l <config-if># authentication order <dot1x / mac /web> l <config-if># authentication port-control <auto / force-auth / force-unauth> l <config-if># authentication radius-attributes vlan reject l <config-if># authentication radius-attributes vlan static l <config-if># authentication reauth l <config-if># authentication timer inactive <60-65535> l <config-if># authentication timer quiet <0-65535> l <config-if># authentication timer reauth <300-4294967294> l <config-if># authentication web l <config-if># authentication web max-login-attempts <3-10> l
<config-if>#
authentication web max-login-attempts infinite |
|
back-pressure |
Enable back-pressure for the specified
interface (Ethernet port/LAG port). Related
Syntax: l
<config-if>#
back-pressure |
|
custom |
<enable> - Enable the custom module
configuration for the specified interface (Ethernet port/LAG port). Related
Syntax: l
<config-if># custom
enable |
|
description |
Write a description for the specified
interface (Ethernet port/LAG port). <WORD> - Enter a description (up to
32 characters). Related
Syntax: l
<config-if># descripton
<WORD> |
|
device-check
|
Perform a device check the specified
interface (Ethernet port/LAG port). ip-address<A.B.C.D> - Enter the IP
address of the device. interval <120/15/30/60>– Check the
device interval by entering the time value. Unit is second. retry < Failure-action
<nothing/powercycle/poweroff> – Set the power cycle. Related
Syntax: l
<config-if>#
device-check ip-address <A.D.C.D> interval <120/15/30/60> retry
< |
|
dos |
Apply DoS to the specified interface
(Ethernet port/LAG port). |
|
dot1x |
It is available for GigabitEthernet port
only. guest-vlan – Set guest VLAN
configuration. max-req <1-10>– Set the maximum
request retries. Default is 2. Port-control
<auto/force-auth/force-unauth>– Set the port control value (auto,
authorized or unauthorized) reauth – Enable/disable the
reauthenctication for this port. timeout <quiet-period / reauth-period
/ server-timeout /supp-timeout /tx-period>– Set timeout value for this
port. <0-65535> - Set a value as quiet
period (default is 60-second). <300-4294967294> - Set a value as
re-authentication period. (default is 3600-second). <1-65535> - Set a value to wait for
a packet retransmission to the authentication server. supp-timeout <1-65535> – Set a vale
as supplicant timeout period. tx-period <1-65535> - Set a value
to wait for a response to an EAP-request / identity before resending the
request. Related
Syntax: l <config-if># dot1x guest-vlan l <config-if># dot1x max-req <1-10> l <config-if># dot1x port-control <auto /force-auth /force-unauth > l <config-if># dot1x reauth l <config-if># dot1x timeout quiet-period <0-65535> l <config-if># dot1x timeout reauth-period <300-4294967294> l <config-if># dot1x timeout server-timeout <1-65535> l <config-if># dot1x timeout supp-timeout <1-65535> l
<config-if># dot1x
timeout tx-period <1-65535> |
|
do |
Run execution commands in current mode. |
|
dray_surveillence |
Use this command to set the ONVIF throughput alert threshold. <16-1000000> - Specify a number as the alert threshold for egress
/ingress throughput. Related Syntax: l <config-if>#dray_surveillence set threshold alert egress <16-1000000> l
<config-if>#dray_surveillence
set threshold alert ingress <16-1000000> |
|
duplex |
Apply the duplex configuration to the
specified interface (Ethernet port/LAG port). <Auto> – Auto
duplex configuration. <Full>– Force full duplex
operation. <Half> – Force half-duplex
operation. Related
Syntax: l
<config-if># duplex
<auto/full/half> |
|
eee |
Apply the EEE configuration to the
specified interface (Ethernet port). |
|
end |
End current mode, change to enable mode
and return to previous phase. |
|
exit |
Exit from current mode. |
|
flowcontrol
|
Configure flow-control mode to the
specified interface (Ethernet port/LAG port). <Auto> – Enable AUTO flow-control
configuration. <Off> – Disable the force
flow-control. <On> – Enable the force
flow-control. Related
Syntax: l
<config-if># flowcontrol
<auto/off/on> |
|
gvrp |
Apply the GVRP configuration to the specified
interface (Ethernet port/LAG port). registration-mode <fixed / forbidden / normal>-
Set registration mode for GVRP. When registration-mode is fixed or forbidden,
it will remove the dynamic port from VLAN. vlan-creation-forbid – Do not remove dynamic port
from VLAN. Related Syntax: l <config-if># gvrp registration-mode <fixed / forbidden / normal> l
<config-if># gvrp
vlan-creation-forbid |
|
ip |
Apply IP configuration to the specified interface
(Ethernet port/LAG port). acl <NAME> - Specify an ACL for packets. Enter
the name of the ACL. arp inspection rate-limit <1-10> – ARP inspection
is to enable Dynamic ARP Inspection function. Set the rate limitation (1 – 10)
on the interface. Vigor switch will drop ARP packets after receives more than
configured rate of packets per second. arp inspection trust – Use it to set trusted
interface. arp inspection validate dst-mac – It means Vigor
switch will drop ARP reply packets if arp-target-mac and ethernet-dst-mac are
not matched. arp inspection validate ip allow-zeros – The
“allow-zeros” means Vigor switch will not drop all zero IP address. arp inspection validate src-mac – It means Vigor
switch will drop ARP requests and reply packets if arp-sender-mac and
ethernet- source-mac are not matched. conflict prevention bind-ip <A.B.C.D> - conflict prevention port-type
DHCP-Client – conflict prevention port-type
DHCP-Client has-server – conflict prevention port-type
DHCP-Server – conflict prevention port-type
DHCP-Server has-server – conflict prevention port-type
Multiple-Hosts – conflict prevention port-type Multiple-Hosts
has-server – conflict prevention port-type Static-Binding – conflict prevention port-type Static-Binding
has-server - dhcp snooping option – Use it to enable the function
of inserting option82 content into the packet. dhcp snooping option action <drop / keep /
replace> - Use it to set the action (drop, keep or replace) when receiving
packets with option82 content. dhcp snooping option circuit-id <STRING> - Use
it to set user-defined circuit-id string (1 to 63 characters). dhcp snooping rate-limit <1-300> - Use it to
set rate limitation on the interface. dhcp snooping trust – Use it to set trusted
interface. dhcp snooping verify mac-address – Use it to verify
MAC address function on the interface. dhcp snooping vlan <1-4094> option circuit-id
<STRING> - Set user-defined circuit-id string for specified VLAN ID. igmp filter <1-128> - Use it to bind a profile
for a port. Specify a profile ID. igmp max-groups <0-256> - Use it to limit port
learning max group number (0-256). igmp max-groups action <deny/replace> - Use it
to set the action (deny or replace) when the number of groups reach the
limitation. source binding max-entry <1-10> - source binding max-entry no-limit - source verify mac-and-ip – Use it to enable IP source
guard function. Related Syntax: l <config-if># ip acl <NAME> l <config-if># ip arp inspection rate-limit <1-10> l <config-if># ip arp inspection trust l <config-if># ip arp inspection validate dst-mac l <config-if># ip arp inspection validate ip allow-zeros l <config-if># ip arp inspection validate src-mac l <config-if># ip conflict prevention bind-ip <A.B.C.D> l
<config-if># ip conflict
prevention port-type DHCP-Client l <config-if># ip conflict prevention port-type DHCP-Client has-server l
<config-if># ip conflict prevention
port-type DHCP-Server l <config-if># ip conflict prevention port-type DHCP-Server has-server l <config-if># ip conflict prevention port-type Multiple-Hosts l <config-if># ip conflict prevention port-type Multiple-Hosts has-server l <config-if># ip conflict prevention port-type Static-Binding l <config-if># ip conflict prevention port-type Static-Binding has-server l <config-if># ip dhcp snooping option l <config-if># ip dhcp snooping option action <drop / keep / replace> l <config-if># ip dhcp snooping option circuit-id <STRING> l <config-if># ip dhcp snooping rate-limit <1-300> l <config-if># ip dhcp snooping trust l <config-if># ip dhcp snooping verify mac-address l <config-if># ip dhcp snooping vlan <1-4094> option circuit-id <STRING> l <config-if># ip igmp filter <1-128> l <config-if># ip igmp max-groups <0-256> l <config-if># ip igmp max-groups action <deny/replace> l <config-if># ip source binding max-entry <1-10> l <config-if># ip source binding max-entry no-limit l
<config-if># ip source verify
mac-and-ip |
|
ipv6 |
Apply IPV6 configuration to the specified
interface (Ethernet port/LAG port). acl <NAME> - Specify the ACL name
for packets mld <filter> – Set IPv6 filter for
MLD configuration. mld max-groups – Specify the number for
maximum group. <0-256> - MLD snooping group
number. action <deny
/replace> –
Define the action to be performed when excessing the maximum group. Related
Syntax: l <config-if># ipv6 acl <NAME> l <config-if># ipv6 mld filter l <config-if># ipv6 mld max-groups <0-256> l
<config-if># ipv6 mld
max-groups action <deny / replace> |
|
lacp |
Apply LACP Configuration to the specified
interface (Ethernet port/LAG port). <1-65535> - Set a number for IEEE
802.3 link aggregation port priority. <long/short> – Set long or short
timeout value. Related
Syntax: l <config-if># lacp port-priority <1-65535> l
<config-if># lacp timeout
<long/short> |
|
lag |
Apply Link Aggregation Group
Configuration the specified
interface (Ethernet port/LAG port). <1-8> - Specify LAG number. Related
Syntax: l
<config-if># lag
<1-8> |
|
loop-protection |
Record the log, shutdown the port or follow the global loop-protection settings for each port. Related Syntax: l <config-if># loop-protection action all l <config-if># loop-protection action global l <config-if># loop-protection action log l <config-if># loop-protection action shutdown |
|
lldp |
med
location -
Configure the LLDP MED location data. The “coordinate”, “civic-address”,
“ecs-elin” locations are independent, so at most three location TLVs could be
sent if their data are not empty. med
network-policy add / remove - Configure
the LLDP MED network policy table. Add /remove a network policy entry that
can be bind to ports. med
tlv-select - Configure
LLDP MED TLVs selection. Available optional TLVs are network-policy,
location, inventory and poe-pse. tlv-select - Select LLDP TLVs to send. <civic-address> - The location is
specified as civic address. <ADDR> -
Range from 6 to 160 hexadecimal bytes. <Coordinate> - The location is
specified as coordinates. <ADDR> - 16
hexadecimal bytes exactly. <ecs-elin> - The location is
specified as ECS ELIN. <ADDR> - 10
to 25 hexadecimal bytes. <IDX_LIST> - Range from 1 to 32. <TLV> - LLDP optional TLV, pick
from: port-desc, sys-name, sys-desc, sys-cap, mac-phy, lag, max-frame-size,
management-addr. pvid <disable/enable> - Enable or
disable the TX optional-TLV 802.1 PVID. vlan-name
<add/remove> <2-4094> - Add/remove a selected VLAN. Enter the VLAN ID
number. <rx> - Enable LLDP reception on
interface. <tx> - Enable LLDP transmission on
interface. Related
Syntax: l <config-if># lldp med location <civic-address/coordinate/ecs-elin> <ADDR> l <config-if># lldp med network-policy add <IDX_LIST> l <config-if># lldp med network-policy remove <IDX_LIST> l <config-if># lldp med tlv-select <network-policy/location/inventory/poe-pse> <network-policy/location/inventory/poe-pse> <network-policy/location/inventory/poe-pse> l <config-if># lldp tlv-select <TLV/pvid/vlan-name> l <config-if># lldp tlv-select pvid <disable/enable> l <config-if># lldp tlv-select vlan-name <add/remove> <2-4094> l
<config-if># lldp
<rx/tx> |
|
mac |
Specify an access control list for
packets. Before configuring, you have to create an
ACL based on MAC address. For example, <config>#
mac acl CA_ACL <config-mac-acl># <NAME> - Enter a name for ACL. Related
Syntax: l
<config-if># mac acl
<NAME> |
|
mvr |
Make MVR configuration. immediate - Enable MVR function. type
<receiver/source> - Specify MVR port
type as receiver or source. Related Syntax: l
<config-if># mvr
immediate l
<config-if># mvr type
<receiver/source> |
|
no |
Negate command. Such command can disable
current setting of command executed and return to the factory setting of that
command. Example: <config-if>
# no mvr The operation will
make mvr setting is default. Continue? [yes/no]:yes <config-if>
# Related
Syntax: l
<config-if># no
<command> |
|
poe |
Enable
or disable the PoE port. |
|
port-security |
port-security - Enable the port security
functionality. Default is disabled. address-limit <1-256>- Enter the number as
limitation for MAC address. action <discard / forward / shutdown> – Speicfy
an action to be performed. Related Syntax: l <config-if># port-security l
<config-if># port-security
adderss-limit <1-256> action <discard / forward / shutdown> |
|
power |
Configure the inline power for the PoE device. inline auto - Turn on the PoE device discovery protocol and apply the power to the devcie. inline never - Turn off the PoE device power. power-limit <15.4w/30w/MW> - Set the power limit for the PoE
device. priority <1-3/critical/high/low> - Set the priority of power
application for the PoE device. schedule-index - Specify the index number of the schedule profile. Related Syntax: l <config-if># power inline auto l <config-if># power inline never l <config-if># power power-limit <15.4w/30w/MW> l <config-if># power priority <1-3/critical/high/low> l <config-if># power schedule-index |
|
protected |
Configure an interface to be a protected
port. Related
Syntax: l
<config-if>#protected |
|
qos |
cos - Configure the default CoS value for
an Ethernet port. <0-7>
- Specify a remark - Configure remarking state of
each port. trust - Configure each port to trust
state while the system is in “basic” mode. There are four trust types for a
device to judge the appropriate queue of the packets. <cos> - Enable cos remarking. <dscp> - Enable DSCP remarking. <cos-dscp> - Enable cos and DSCP
remarking. <precedence> - Enable IP precedence
remarking. Related
Syntax: l <config-if>#qos cos <0-7> l <config-if>#qos remark <cos/dscp/precedence> l
<config-if>#qos trust
<cos/cos-dscp/ dscp/precedence> |
|
rate-limit |
It is effective for Ethernet port only. egress - Configure the egress port
shaper. ingress - Configure the ingress port
shaper. egress queue – Configure queue for egress
port shaper. <0-1000000>
- Enter a number
as the average traffic rate in Kbps. It must be a multiple of 16. <16-1000000> - Enter a number as the average traffic rate in Kbps. It must be
a multiple of 16. <1-8> - Specify a nubmer as queue
ID. Related
Syntax: l <config-if># rate-limit egress <0-1000000> l <config-if># rate-limit egress queue <1-8> <16-1000000> l
<config-if># rate-limit ingress
<16-1000000> |
|
shutdown |
Disable the selected interface. Example: (config)#
interface gigabitethernet 3 (config-if)#
shutdown (config-if)#
exit (config)#
exit # show
interface Gigabitethernet 3 GigabitEthernet3
is down Related
Syntax: l
<config-if># shutdown |
|
spanning-tree
|
Configure spanning-tree settings. bpdu-filter - Set the BPDU-Filter for
specified port. bpdu-guard - Set the BPDU-Guard for
specified port. edge - Set the edge-port for specified
port. cost - Change an interface’s spanning
tree path cost. link-type - Specify a link type for
spanning tree protocol use. mcheck - Set the mcheck for specified
port to migrate. mst - Set spanning-tree parameters of
instance. port-priority- Set the priority for
specified instance. <0-200000000> - Specify a value of
internal path cost (0 means Auto). <point-to-point> - The selected
port will be treated as point-to-point. <shared> - The selected port will
be treated as shared. <0-15> - Specify an instance ID. <0-240> - Specify a priority number
for the selected port. Related
Syntax: l <config-if># spanning-tree <bpdu-filter /bpdu-guard/ edge> l <config-if># spanning-tree cost <0-200000000> l <config-if># spanning-tree link-type <point-to-point/shared> l <config-if>#spanning-tree mcheck l <config-if>#spanning-tree mst <0-15> cost <0-200000000> l
<config-if># spanning-tree
port-priority <0-240> |
|
speed |
Configure speed operation. <10/100/1000> - Force 10/100/1000
Mbps operation. <auto> - Enable Auto speed
configuration. Related
Syntax: l <config-if># speed<10/100/1000> l
<config-if># speed auto |
|
storm-control
|
action - Select an action for storm
control after exceeding the threshold. broadcast level - Enable the storm
control type of broadcast for the selected port. unknown-multicast level - Enable the
storm control type of unknown-multicast for the selected port. unknown-unicast level- Enable the storm
control type of unknown-unicast for the selected port. <drop> - Drop packets after
exceeding storm control threshold. <shutdown> - Disable the port after
exceeding storm control threshold. <1-1000000> - Specify the rate
value. Related
Syntax: l <config-if># storm-control action <drop/shutdown> l <config-if># storm-control broadcast level <1-1000000> l <config-if># storm-control unknown-multicast level <1-1000000> l
<config-if># storm-control
unknown-unicast level <1-1000000> |
|
surveillance-vlan |
cos - Set
surveillance VLAN configuration. mode - Set
surveillance member port join mode. <all> - QoS attributes are applied
to all packets that are classified to the Surveillance VLAN. <src> - QoS attributes are applied
only on packets from IP phones. <auto> - Make surveillance member
port join voice VLAN automatically. <manual> - The administrator
manually makes surveillance member port join voice VLAN. Related Syntax: l <config-if># surveillance-vlan cos <all/src> l
<config-if># surveillance-vlan mode <auto/manual> |
|
switchport |
Set switching mode characteristics. access
vlan –Use it to set a native VLAN on the interface. default-vlan
tagged – Use it to make the selected port interface to become the default
VLAN tagged member. forbidden
default-vlan – Use it to forbid the defult-vlan on the interface. forbidden
vlan - Use it to forbid a vlan on the interface. hybrid
accetable-frame-type – Use it to choose which type of frame will be accepted. hybrid
allowed – Use it to allow a VALN set on the interface. hybrid ingress-filtering – Use it to enable VLAN
ingress filter. hybrid
pvid – Use it to set PVID of the interface. mode
access - Use it to configure the selected port as the role of access. Only
untagged frames will be accepted. mode
hybrid - Use it to configure the selected port as the role of hybrid. Support
all functions defined in IEEE 802.1Q specification. mode
trunk uplink – Use it to configure the selected port as the role of trunk. It
can recognize double tagging on the interface. trunk
allowed – Use it to allow a VALN on the interface. trunk
native – Use it to set a native VLAN on the interface. tunnel
vlan – Use it to set a Dot1q tunnel VLAN on the interface. vlan tpid – Use it to set TPID on the interface. <1-4094>
- Specify a VLAN ID. <add/remove>
- Add or remove the allowed VLAN list. <all/tagged-only/untagged-only>
- Specify an option for accepting all frames, only tagged frames or only
untagged frames. <1-4094/all>
- Specify a VLAN ID or all VLAN IDs. < 0x8100 / 0x Related
Syntax: l <config-if># switchport access vlan <1-4094> l <config-if># switchport default-vlan tagged l <config-if># switchport forbidden default-vlan l <config-if># switchport forbidden vlan <add/remove> <1-4094> l <config-if># switchport hybrid accetable-frame-type <all/tagged-only/untagged-only> l <config-if># switchport hybrid allowed vlan add <1-4094> l <config-if># switchport hybrid allowed vlan add <1-4094> <tagged/ untagged> l <config-if># switchport hybrid allowed vlan remove <1-4094> l <config-if># switchport hybrid ingress-filtering l <config-if># switchport hybrid pvid <1-4094> l <config-if># switchport mode <access/hybrid> l <config-if># switchport mode trunk uplink l <config-if># switchport trunk allowed vlan <add /remove> <1-4094/all> l <config-if># switchport trunk native <1-4094> l <config-if># switchport tunnel vlan <1-4094> l
<config-if># switchport
vlan tpid < 0x8100/0x |
|
udld |
Configure UDLD enabled or disabled and
ignore global UDLD setting. aggressive - Enable UDLD protocol on such
interface. Related Syntax: l <config-if># udld l
<config-if># udld
aggressive |
|
vlan |
mac-vlan group - Set a MAC-based VLAN configuration. protocol-vlan
group - Set a
protocol-based VLAN configuration. <1-2147483647>
- Specify a group ID to map. <1-4094>
- Specify a VLAN ID. Related
Syntax: l
<config-if># vlan mac-vlan group
<1-2147483647> vlan <1-4094> l
<config-if># vlan protocol-vlan
group<1-2147483647> vlan <1-4094> |
|
voice-vlan |
cos - Set voice VLAN configuration as COS
mode. mode - Set voice
member port join mode. <all> - QoS attributes are applied
on all packets that are classified to the Voice VLAN. <src> - QoS attributes are applied
only on packets from IP phones. <auto> - Make voice member port
join voice VLAN automatically. <manual> - The administrator
manually makes voice member port join voice VLAN. Related
Syntax: l
<config-if># voice-vlan cos
<all/src> l
<config-if># voice-vlan mode
<auto/manual> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# interface LAG 1 G2280(config-if)# speed 100 G2280(config-if)# backpressure G2280(config-if)# lldp med location ecs-elin
112233445566778899AA G2280(config-if)#
vlan mac-vlan group 35 vlan 1000 G2280(config-if)# |
Telnet Command: ip
Use
this command to create an IPv4 access list (ACL) which performs classification on layer 3 fields and enters ip-access
configuration mode.
Syntax Items
ip acl
ip arp
ip conflict
ip dhcp
ip igmp
ip source
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
ip acl |
acl <NAME> - Set the name of the
access list (ACL) based on IPv4. To configure detailed settings, enter the
name of ACL to access into next level. <config>#ip
acl <NAME> Then, available sub-command includes: <config-ip-acl>#deny <config-ip-acl>#do <config-ip-acl>#end <config-ip-acl>#exit <config-ip-acl>#permit <config-ip-acl>#sequence <config-ip-acl>#show |
|
Use the “deny” command to create deny
rules for the IPv4 access list. <0-255/egp/hmp/icmp/igp/ipinip/ipv6
/ipv6:frag /ipv6:icmp /ipv6:rout / ip / l2tp /ospf /pim / rdp / rsvp /tcp
/udp > - Specify the IP protocol number or enter the name of the protocol. <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D>
<A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> -
Specify the source and destination IPv4 addresses and subnet masks. dscp <0-63> - Set the DSCP
filtering by specifying a value for DSCP. precedence <0-7> - Set the cos
value and the cos mask for a packet. shutdown – Disable the Ethernet
interface. any – Any IP address (as source or
destination). Related
Syntax: l <config-ip-acl >#deny <0-255> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> dscp <0-63> l <config-ip-acl >#deny <0-255> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ip-acl >#deny <0-255> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> precedence <0-7> l <config-ip-acl >#deny <0-255> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ip-acl >#deny <0-255> any <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> dscp <0-63> l <config-ip-acl >#deny <0-255> any <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ip-acl >#deny <0-255> any <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> precedence <0-7> l <config-ip-acl >#deny <0-255> any <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ip-acl >#deny <0-255> any any dscp <0-7> l <config-ip-acl >#deny <0-255> any any dscp <0-7> shutdown l <config-ip-acl >#deny <0-255> any any precedence <0-7> l
<config-ip-acl >#deny
<0-255> any any precedence <0-7> shutdown |
|
|
Use the “do” command to run execution
command in current mode. <SEQUENCE> - Related
Syntax: l
<config-ip-acl>#do <SEQUENCE> |
|
|
Use the “end” command to finish current
mode. Any changes in current mode will be saved. Related
Syntax: l
<config-ip-acl>#end |
|
|
Use the “exit” command to close the
current CLI session or return to the previous mode without saving the
settings. Related
Syntax: l
<config-ip-acl>#exit |
|
|
Use the “no sequence” command to delete
any entry in management ACL. <1-2147483647>- Specify an index
number of the ACL. Related
Syntax: l
<config-ip-ayl>#no sequence
<1-2147483647> |
|
|
Use the “permit” command to create permit
rules which bypass the packets meet the rule. <0-255/egp/hmp/icmp/igp/ipinip/ipv6
/ipv6:frag /ipv6:icmp /ipv6:rout / ip / l2tp /ospf /pim / rdp / rsvp /tcp
/udp > - Specify the IP protocol number or enter the name of the protocol. <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D>
<A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> -
Specify the source and destination IPv4 addresses and subnet masks. dscp <0-63> - Set the DSCP
filtering by specifying a value for DSCP. precedence <0-7> - Set the cos
value and the cos mask for a packet. Shutdown – Disable the Ethernet
interface. any – Any IP address (as source or
destination). Related
Syntax: l <config-ip-acl >#permit <0-255> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> dscp <0-63> l <config-ip-acl >#permit <0-255> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ip-acl >#permit <0-255> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> precedence <0-7> l <config-ip-acl >#permit <0-255> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ip-acl >#permit <0-255> any <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> dscp <0-63> l <config-ip-acl >#permit <0-255> any <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ip-acl >#permit <0-255> any <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> precedence <0-7> l <config-ip-acl >#permit <0-255> any <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ip-acl >#permit <0-255> any any dscp <0-7> l <config-ip-acl >#permit <0-255> any any dscp <0-7> shutdown l <config-ip-acl >#permit <0-255> any any precedence <0-7> l
<config-ip-acl >#permit
<0-255> any any precedence <0-7> shutdown |
|
|
Use the “sequence” command to deny or permit the ACL. <1-2147483647> - Enter the sequence of ACL
entry. The sequence represents the priority of the ACE in the ACL. Related Syntax: l <config-ip-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647> deny l
<config-ip-acl
>#sequence <1-2147483647> permit |
|
|
Use the “show acl” command to list
current status of the selected ACL. |
|
|
ip arp |
Use this command to enable the function
of dynamic ARP inspection. vlan <1-4094> - Specify the VLAN ID
number. Related
Syntax: l <config>#ip arp inspection l
<config>#ip arp
inspection vlan <1-4094> |
|
ip conflict |
Use this command to do IP conflict prevention. lag - Enable/disable the function. <A.B.C.D> - Specify the IPv4 addresses. <1-10> - Specify a physical port. <1-8> - Specify a LAG port. Related Syntax: l <config>#ip conflict lag l <config>#ip conflict prevention l <config>#ip conflict prevention clear l <config>#ip conflict prevention server-ip <A.B.C.D> interface GigabitEthernet <1-10> l
<config>#ip conflict
prevention server-ip <A.B.C.D> interface LAG <1-8> |
|
ip dhcp |
Use this command to enable DHCP client to
get IP address from remote DHCP server. database <flash/tftp/timeout/write-delay>
- Write the database to FLASH or remote TFTP server. Set timeout interval for
abortion. Set delay timer for writing to URL. <A.B.C.D> - Specify the IPv4
addresses. <HOSTNAME> - Enter the name of the
host. <NAME> - Set a name for the backup
file. <0-86400> - Enter a value. Unit is
second. <15-86400> - Enter a value. Unit is
second. option – Configure DHCP-Option82 settings
by specifying remote ID number. <STRING> - Enter a string (from 1
to 63 characters) for the DHCP option. vlan – Configure VLAN settings. <1-4094> - Specify the VLAN ID
number. Related
Syntax: l <config>#ip dhcp snooping l <config>#ip dhcp snooping database l <config>#ip dhcp snooping database flash l <config>#ip dhcp snooping database tftp <A.B.C.D> l <config>#ip dhcp snooping database tftp <HOSTNAME><NAME> l <config>#ip dhcp snooping database timeout <0-86400> l <config>#ip dhcp snooping database write-delay <15-86400> l <config>#ip dhcp snooping option remote-id <STRING> l
<config>#ip dhcp
snooping vlan <1-4094> |
|
ip igmp |
Use this command to set IGMP profile and
enable IGMP snooping function. Profile – Set IGMP profile. <1-128> - Enter the index number of
IGMP profile to access into next phase for configuring detailed settings. <A.B.C.D><A.B.C.D> - Specify
the source and destination IPv4 addresses action <deny/permit> - Speicfy the
rule (deny/permit) for the IGMP profile. Related
Syntax: l <config>#ip igmp profile <1-128> <config-igmp-profile>#
do <config-igmp-profile>#
end <config-igmp-profile>#
exit <config-igmp-profile>#
profile range ip <A.B.C.D><A.B.C.D> <config-igmp-profile>#
profile range ip <A.B.C.D><A.B.C.D> action <deny/permit> <config-igmp-profile>#
profile range ip <A.B.C.D> action <deny/permit> <config-igmp-profile>#
show l
<config>#ip igmp
snooping |
|
ip source |
Use
this command to create a static IP source binding entry. <A:B:C:D:E:F> - Enter the MAC address for the binding
entry. vlan <1-4094> -
Specify the VLAN ID number. <A.B.C.D><A.B.C.D>
- Specify the source and destination IPv4 addresses <1-10>
- Specify a physical port. <1-8>
- Specify a LAG port. Related Syntax: l
<config>#ip
source binding <A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> <A.B.C.D>
<A.B.C.D> interface Gigabitethernet <1-10> l
<config>#ip
source binding <A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> <A.B.C.D>
<A.B.C.D> interface LAG <1-8> l
<config>#ip
source binding vlan <1-4094> <A.B.C.D> <A.B.C.D> interface
Gigabitethernet <1-10> l
<config>#ip
source binding vlan <1-4094> <A.B.C.D> <A.B.C.D> interface
LAG <1-8> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# ip acl market_1 G2280(config-ip-acl)# G2280(config-ip-acl)# deny 20
192.168.2.55/255.255.255.0 192.168.2.85/255 G2100(config)# ip dhcp snooping database tftp draytek
carrie_backup |
Telnet Command: ipv6
Use this command to create an IPv6 access list (ACL).
Syntax Items
ipv6
ipv6 acl
ipv6 mld
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
ipv6
acl |
<NAME> - Set the name of the access
list (ACL) based on IPv6. To configure detailed settings, enter the
name of ACL to access into next level. <config>#ipv6
acl <NAME> Then, available sub-command includes: <config-ipv6-acl>#deny <config-ipv6-acl>#do <config-ipv6-acl>#end <config-ipv6-acl>#exit <config-ipv6-acl>#no <config-ipv6-acl>#permit <config-ipv6-acl>#sequence <config-ipv6-acl>#show |
|
Use the “deny” command to create deny
rules for the IPv4 access list. <0-255/icmp/ipv6/tcp /udp > -
Specify the IP protocol number or enter the name of the protocol. <0-255/any> - Specify ICMPv6
number. <X:X::X:X>/<0-128>
<X:X::X:X>/<0-128> -
Specify the source/destination IPv6 addresses and subnet masks. dscp <0-63> - Set the DSCP
filtering by specifying a value for DSCP. precedence <0-7> - Set the cos
value and the cos mask for a packet. shutdown – Disable the Ethernet
interface. any – Any IP address (as source or
destination). <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime
/ discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin /
kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet /
time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 /
PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data
/ hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog /
tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> - Set TCP port. match-all <TCP_FLAG> - Set TCP
flags. List of TCP flags that should occur. If a flag should be set, it is p
refixed by "+".If a flag should be unset, it is prefixed by
"-". Avai lable options are +urg, +ack, +psh, +rst, +syn, +fin,
-urg, -ack, -psh, -rst, -syn and -fin.To define more than 1 flag - enter
additional flags one after another without a space (example +syn-ack). <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc /
bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp
/ snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who>
<X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps
/ discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp /
snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> - Set
UDP port. Related
Syntax: l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any precedence <0-7>shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >deny icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255/any> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128><0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255/any> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128><0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255/any> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128><0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255/any> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128><0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255/any> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any <0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255 /any> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any <0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255 /any> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any <0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255 /any> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any <0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255 /any> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any <0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255 /any> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any precedence <0-7>shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 any <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 any <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 any <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 any <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 any <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 any <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 any any l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 any any dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 any any dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 any any precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 any any precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny ipv6 any any shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> match-all <TCP_FLAG> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> match-all <TCP_FLAG> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> match-all <TCP_FLAG> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> match-all <TCP_FLAG> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> match-all <TCP_FLAG> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny udp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny udp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny udp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny udp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> dscp <0-63> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny udp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> dscp <0-63> precedence <0-7> shutdown l
<config-ipv6-acl >#deny
udp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535> any |
|
|
Use the “do” command to run execution
command in current mode. <SEQUENCE> - Related
Syntax: l
<config-ipv6-acl>#do <SEQUENCE> |
|
|
Use the “end” command to finish current
mode. Any changes in current mode will be saved. Related
Syntax: l
<config-ipv6-acl>#end |
|
|
Use the “exit” command to close the
current CLI session or return to the previous mode without saving the
settings. Related
Syntax: l
<config-ipv6-acl>#exit |
|
|
Use the “no sequence” command to delete
any entry in management ACL. <1-2147483647>- Specify an index
number of the ACL. Related
Syntax: l
<config-ip-acl>#no sequence
<1-2147483647> |
|
|
Use the “permit” command to create permit
rules which bypass the packets meet the rule. <0-255/icmp/ipv6/tcp /udp > -
Specify the IP protocol number or enter the name of the protocol. <0-255/any> - Specify ICMPv6
number. <X:X::X:X>/<0-128>
<X:X::X:X>/<0-128> -
Specify the source/destination IPv6 addresses and subnet masks. dscp <0-63> - Set the DSCP
filtering by specifying a value for DSCP. precedence <0-7> - Set the cos
value and the cos mask for a packet. shutdown – Disable the Ethernet
interface. any – Any IP address (as source or
destination). <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime
/ discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin /
kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet /
time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 /
PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data
/ hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog /
tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> - Set TCP port. match-all <TCP_FLAG> - Set TCP
flags. List of TCP flags that should occur. If a flag should be set, it is p
refixed by "+".If a flag should be unset, it is prefixed by
"-". Avai lable options are +urg, +ack, +psh, +rst, +syn, +fin,
-urg, -ack, -psh, -rst, -syn and -fin.To define more than 1 flag - enter
additional flags one after another without a space (example +syn-ack). <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc /
bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp
/ snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who>
<X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc /
bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp
/ snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> - Set
UDP port. Related
Syntax: l <config-ipv6-acl >#permit <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any precedence <0-7>shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit <0-255> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl > permit icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255/any> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128><0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255/any> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128><0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255/any> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128><0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255/any> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128><0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255/any> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any <0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255 /any> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any <0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255 /any> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any <0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255 /any> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any <0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255 /any> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit icmp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any <0-255 / any / destination-unreachable / echo-reply / echo-request / nd-na / nd-ns / packet-too-big/ parameter-problem/ router-advertisement / router-solicitation / time-exceeded> <0-255 /any> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any precedence <0-7>shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> any shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 any <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 any <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 any <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 any <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 any <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 any <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 any any l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 any any dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 any any dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 any any precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 any any precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit ipv6 any any shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl >#deny tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> match-all <TCP_FLAG> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> match-all <TCP_FLAG> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> match-all <TCP_FLAG> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> match-all <TCP_FLAG> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> match-all <TCP_FLAG> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> precedence <0-7> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit tcp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535 / PORT_RANGE / any / daytime / discard / domain / drip / echo / ftp / ftp-data / hostname / klogin / kshell / pop2 / pop3 / smtp / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / telnet / time / whois / www> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit udp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit udp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> dscp <0-63> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit udp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> dscp <0-63> shutdown l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit udp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> dscp <0-63> precedence <0-7> l <config-ipv6-acl ># permit udp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535/ PORT_RANGE / any / bootpc / bootps / discard / domain / echo / nameserver / netbios-ns / ntp / rip / snmp / snmptrap / sunrpc / syslog / tacacs-ds / talk / tftp / time / who> dscp <0-63> precedence <0-7> shutdown l
<config-ipv6-acl >#
permit udp <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> <0-65535> any |
|
|
Use the “sequence” command to deny or permit the ACL. <1-2147483647> - Enter the sequence of ACL
entry. The sequence represents the priority of the ACE in the ACL. Related Syntax: l <config-ipv6-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647> deny l
<config-ipv6-acl
>#sequence <1-2147483647> permit |
|
|
Use the “show acl” command to list current status of
the selected ACL. |
|
|
ipv6 mld |
Use
this command to set MLD configuration. profile <1-128> - Use
it to enter profile configuration. snooping – Use it to enable
MLD snooping function. forward-method
<dip/mac> - report-suppression –
Use it to enable MLD snooping report-suppression function. unknown-multicast
action <drop/flood/router-port> - Use it to set unknown multicast
action. version <1/2> – Use it
to change MLD support version. vlan <1-4094> - Use
it to enable MLD on VLAN. Specify a VLAN ID for configuration. forbidden-port
GigabitEthernet <1-10> - Specify a physical port. forbidden-port LAG <1-8> - Specify a LAG port. forbidden-router-port
GigabitEthernet <1-10> - Use it to add static forbidden router port. Specify
a physical port. forbidden-router-port
LAG <1-8> - Use it to add static forbidden router port. Specify a LAG
port. immediate-leave –
Use it to enable fastleave function. last-member-query-count
<1-7> - Use it to change how many query packets will send. Specify the
last member query count. Default is 2. last-member-query-interval
<1-25> - Use it to set interval between each query packet. Specify the
last member query interval. Default is 1. query-interval
<30-18000> - Use it to set interval between each query. Specify the
query interval. Default is 125. response-time
<5-20> - Use it to set response time. Specify a time value. Default is
10. robustness-variable
<1-7> - Specify a robustness-variable value. Default is 2. router learn pim-dvmrp –
Use it to enable learning router port by rouing protocol packets (DVMRP). static-group
<X:X::X:X> interfaces gigabitethernet <1-10> - Use it to add a
static group. Specify a physical port. static-group
<X:X::X:X> interfaces LAG <1-8> - Use it to add a static group. Specify
a LAG port. static-port
gigabitethernet <1-10>- Use it to add static forwarding port. Specify a
physical port. static-port
LAG <1-8>- Use it to add static forwarding port. Specify a LAG port. static-router-port
Gigabitethernet <1-10> - Use it to add static router port. All query
packets wil forward to the specified port. Specify a physical port. static-router-port
LAG <1-8> - Use it to add static router port. All query packets wil
forward to the specified port. Specify a LAG port. Related Syntax: l
<config>#ipv6
mld profile <1-128> <config-mld-profile>#
do <config-mld-profile>#
end <config-mld-profile>#
exit <config-mld-profile>#
profile range ipv6 <X:X::X:X> action <deny/permit> <config-mld-profile>#
profile range ipv6 <X:X::X:X> <X:X::X:X> <config-mld-profile>#
profile range ipv6 <X:X::X:X> <X:X::X:X> action
<deny/permit> <config-mld-profile>#
show l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping forward-method <dip/mac> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping report-suppression l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping unknown-multicast action <drop/flood/router-port> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping version <1/2> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> forbidden-port Gigabitethernet <1-10> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> forbidden-port LAG <1-8> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> forbidden-router-port Gigabitethernet
<1-12> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> forbidden-router-port LAG <1-8> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> immediate-leave l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> last-member-query-count <1-7> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> last-member-query-interval <1-25> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> query-interval <30-18000> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> response-time <5-20> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> robustness-variable <1-7> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> router learn pim-dvmrp l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> static-group <X:X::X:X> interfaces
gigabitethernet <1-10> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> static-group <X:X::X:X> interfaces LAG
<1-8> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> static-port gigabitethernet <1-10> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> static-port LAG <1-8> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> static-router-port Gigabitethernet
<1-10> l
<config>#ipv6
mld snooping vlan <1-4094> static-router-port LAG <1-8> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# ipv6 mld snooping vlan 33 G2100(config)# ipv6 acl CA_v6 G2100(config-ipv6-acl)#
deny 3 00:50::32:ff/24 00:50::78:aa/32 |
Telnet Command: lacp
Use this command to set the system
priority of the switch.
Syntax Items
lacp
lacp system-priority
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
lacp |
Enable the function. |
|
lacp system-priority |
It is used for selelcting a master switch
between two devices. Lower system priority has higher priority. The device
with higher priority value can determine which port is able to join LAG. <1-65535>
- Specify the system priority value. Related
Syntax: l <config># lacp l
<config># lacp system-priority <1-65535> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# lacp system-priority 1000 G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: lag
LAG port can transmit packets to
all ports for balancing the traffic loading. Use this command to change the
load balance algorithm to src-dst-mac or src-dst-mac-ip as the Load Balance
policy.
Syntax Items
lag load-balance
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
lag load-balance |
LAG load balancing is based on source and
destination MAC address and/or IP address. Related
Syntax: l <config># lag load-balance src-dst-mac l
<config># lag
load-balance src-dst-mac-ip |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: lldp
Use this command to set LLDP
function.
Syntax Items
lldp
lldp holdtime-multiplier
lldp lldpdu
lldp med
lldp reinit-delay
lldp tx-delay
lldp tx-interval
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
lldp |
Enable the function of LLDP. |
|
lldp
holdtime-multiplier |
Set the multiplier used for calculating the
LLDP discovery packet hold time. <2-10> - Set the LLDP hold time
multiplier. Related
Syntax: l
<config># lldp holdtime-multiplier <2-10> |
|
lldp
lldpdu |
bridging - The LLDP packets will be
bridging when LLDP is disabled. filtering - The LLDP packets will be
filtered and deleted when LLDP is disabled. flooding - The LLDP packets will be flooded and forwarded to all
interfaces when LLDP is disabled. Related
Syntax: l <config># lldp lldpdu bridging l <config># lldp lldpdu filtering l
<config># lldp lldpdu flooding |
|
lldp
med |
med fast-start-repeat-count - Set the
LLDP PDU fast start TX repeat count. med network-policy - Set the LLDP MED
network policy table. med network-poicy voice auto - Enable the
network policy voice auto mode. <1-10> - Set the fast start repeat
count. <1-32> - Specify the index number
of the policy. app <guest-voice/ gust-voice-signaling
/ softphone-voice / streaming-video / video-conferencing / video-signaling /
voice / voice-signaling> - Configure the application type for the policy. vlan <1-4094> - Specify the VLAN
ID. vlan-type
<tag/untag> - Set the VLAN tag status. priority <0-7> - Specify the L2
priority. dscp <0-63> - Specify the DSCP
value. Related
Syntax: l <config># lldp med fast-start-repeat-count <1-10> l <config># lldp med network-policy <1-32> app< guest-voice/ gust-voice-signaling / softphone-voice / streaming-video / video-conferencing / video-signaling / voice / voice-signaling > vlan <1-4094> vlan-type <tag/untag> priority <0-7> dscp <0-63> l
<config># lldp med network-poicy
voice auto |
|
lldp
rinit-delay |
Set the LLDP re-initial delay to avoid
LLDP generating too many PDU. <1-10> - Specify a number for LLDP
server to initialize. Related Syntax: l
<config># lldp rinit-delay
<1-10> |
|
lldp
tx-delay |
Set the delay time between the successful
LLDP frame transmissions. <1-8191> - Enter the number of
delay time. Note that both tx-interval and tx-delay
will affect the LLDP Related
Syntax: l
<config># lldp tx-delay
<1-8191> |
|
lldp
tx-interval |
Set the LLDP TX interval. <5-32767> - Enter the interval in
unit of second. Related
Syntax: l
<config># lldp tx-interval
<5-32767> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# lldp med network-policy 30 app
guest-voice vlan 30 vlan-type untag priority 3 dscp G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: logging
Use this command to set logging
service on VigorSwitch.
Syntax Items
logging
logging buffered
logging console
logging file
logging host
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
logging |
Enable the logging service. |
|
logging
buffered |
Store the log message in the RAM. |
|
logging
console |
Specify the logging level. <0-7> - Specify the logging level
by entering a number (from EMEGR-DEBUG). Related
Syntax: l <config># logging console l
<config># logging console
severity <0-7> |
|
logging
file |
Store the log message in the flash. <0-7> - Specify the logging level
by entering a number (from EMEGR-DEBUG). Related
Syntax: l
<config># logging file severity
<0-7> |
|
logging
host |
Define the logging server. host <A.B.C.D> - Enter an IP
address of the remote (or local) server. facility <local0-local7> - Specify
the facility parameter for the syslog message. port <1-65535> - Enter a number for
the remote server. Default is 514. severity <0-7> - Specify the
logging level by entering a number (from EMEGR-DEBUG). <HOSTNAME> - Define a name as the
host. Related
Syntax: l <config>#logging host <A.B.C.D> facility <local0-local7> l <config>#logging host <A.B.C.D> port <1-65535> l <config>#logging host <A.B.C.D> port <1-65535> facility <local0-local7> l <config>#logging host <A.B.C.D> port <1-65535> severity <0-7> facility <local0-local7> l <config>#logging host <A.B.C.D> severity <0-7> facility <local0-local7> l <config>#logging host <HOSTNAME> facility <local0-local7> l <config>#logging host <HOSTNAME> port <1-65535> l <config>#logging host <HOSTNAME> port <1-65535> facility <local0-local7> l <config>#logging host <HOSTNAME> port <1-65535> severity <0-7> facility <local0-local7> l <config>#logging host <HOSTNAME> severity <0-7> facility <local0-local7> l <config>#logging host <X:X::X:X> facility <local0-local7> l <config>#logging host <X:X::X:X> port <1-65535> l <config>#logging host <X:X::X:X> port <1-65535> facility <local0-local7> l
<config>#logging host
<X:X::X:X> port <1-65535> severity <0-7> facility
<local0-local7> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# logging host aa:00:: |
Telnet Command: logmail
Use this command to configure log
mail.
Syntax Items
logmail active
logmail auth
logmail category
logmail encry
logmail password
logmail port
logmail receiver
logmail sender
logmail server
logmail username
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
logmail
active |
<disable/enable>
- Enable or disable the function of
log mail. Related
Syntax: l
<config># logmail active
<disable/enable> |
|
logmail
auth |
<disable/enable>
- Enable or disable the function of
SMTP server authentication. Related
Syntax: l
<config># logmail auth
<disable/enable> |
|
logmail
category |
<AAA, ACL,
AUTHMGR,CABLE_DIAG, DAI, DHCP_SNOOPING, GVRP, IGMP_SNOOPING, IPSG, L2, LLDP,
Mac-based, Mirror, MLD_SNOOPING, Platform, PM, POE, Port, PORT_SECURITY, QoS,
Rate, SNMP, STP, Security, System, Surveillance, Trunk, UDLD, VLAN, CLEAR>
- Specify one type for the logmail. Related
Syntax: l
<config># logmail category
<AAA, ACL, AUTHMGR,CABLE_DIAG, DAI, DHCP_SNOOPING, GVRP, IGMP_SNOOPING, IPSG,
L2, LLDP, Mac-based, Mirror, MLD_SNOOPING, Platform, PM, POE, Port,
PORT_SECURITY, QoS, Rate, SNMP, STP, Security, System, Surveillance, Trunk,
UDLD, VLAN, CLEAR> |
|
logmail
encry |
<disable/ssltls/starttls>
- Specify the encryption type for mail alert. Related
Syntax: l
<config># logmail encry <disable/
ssltls/starttls> |
|
logmail
password |
<PASSWORD>
- Enter the password for SMTP server authentication. Related
Syntax: l
<config># logmail password <PASSWORD> |
|
logmail
port |
<0-65535>-
Enter a port number. Related
Syntax: l
<config># logmail port <0-65535> |
|
logmail
receiver |
Specify an
address for receiving the alart mail. <ADDRESS>
- Enter the email address of the receiver. Related
Syntax: l
<config># logmail receiver <ADDRESS> |
|
logmail
sender |
Specify an
address which sends out the alert mail. <ADDRESS>
- Enter the email address of the sender. Related
Syntax: l
<config># logmail |
|
logmail
server |
Set the IP
address of the server. <ADDRESS>
- Enter the IP address of the SMTP server. Related
Syntax: l
<config># logmail server <ADDRESS> |
|
logmail
username |
<NAEM> -
Enter the username authenticated by STMP server. Related
Syntax: l
<config># logmail username <NAME> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# logmail receiver [email protected] G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: loop-protection
Use this command to set
loop-protection.
Syntax Items
loop-protection action
loop-protection periodicTime
loop-protection state
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
loop-protection
action |
Specify an action to be taken when the
loop is happened. <all/log/shutdown> - Specify one
action to be executed. Related
Syntax: l
<config># loop-protection action
<all/log/shutdown> |
|
loop-protection
periodicTime |
Send the loop protection packets to the
network hosts. <1-3> - Enter the number of the
packet. Related
Syntax: <config>#
Related Syntax: l
<config># loop-protection periodicTime
<1-3> |
|
loop-protection
state |
<enable/disable> - Enable or
disable the function of loop protection. Related
Syntax: l
<config># loop-protection state
<enable/disable> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# loop-protection state enable G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: mac
Use this command to create a MAC
access list.
Syntax Items
mac acl
mac address-table
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
mac acl |
<NAME> - Set the name of the access
list (ACL). To configure detailed settings, enter the
name of ACL to access into next level. <config>#mac
acl <NAME> Then, available sub-commands are: <config-mac-acl>#deny <config-mac-acl>#do <config-mac-acl>#end <config-mac-acl>#exit <config-mac-acl>#permit <config-mac-acl>#sequence |
|
Use the “deny” command to add deny rules
for the MAC access list: <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> - Specify the source and destination MAC
addresses and subnet masks. cos <0-7><0-7> - Set the cos
value and the cos mask for a packet. <0x0600-0xFFFF> - Set the EtherType
of the packet. Shutdown – Disable the Ethernet
interface. vlan <1-4094> - Specify the VLAN ID
of the packet. any – Any MAC address. Related
Syntax: l
<config-mac-acl >#deny <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7> l
<config-mac-acl >#deny <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>
ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl >#deny <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>
ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> shutdown l
<config-mac-acl >#deny <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>
shutdown l
<config-mac-acl >#deny <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl ># deny <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF>
shutdown l
<config-mac-acl ># deny <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> shutdown l
<config-mac-acl >#deny any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7> l
<config-mac-acl >#deny any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>
ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl >#deny any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>
ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> shutdown l
<config-mac-acl >#deny any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>
shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any cos <0-7><0-7> l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any cos <0-7><0-7> shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any vlan <1-4094> l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any vlan <1-4094> cos <0-7><0-7> l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any vlan <1-4094> cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any vlan <1-4094> cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any vlan <1-4094> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#deny any any vlan <1-4094> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> shutdown l
<config-mac-acl >#deny
any any vlan <1-4094> shutdown |
|
|
Use the “do” command to run execution command in
current mode. <SEQUENCE> - Related Syntax: l
<config-mac-acl>#do <SEQUENCE> |
|
|
Use the “end” command to finish current mode. Any
changes in current mode will be saved. Related Syntax: l
<config-mac-acl>#end |
|
|
Use the “exit” command to close the current CLI
session or return to the previous mode without saving the settings. Related Syntax: l
<config-mac-acl>#exit |
|
|
Use the “no sequence” command to delete any entry in
management ACL. <1-65535>- Specify an index number of the ACL. Related Syntax: l
<config-mac-acl>#no sequence
<1-65535> |
|
|
Use the “permit” command to add permit rules which
bypass the packets meet the rule. <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
>- Specify the source
and destination MAC addresses and subnet masks. cos <0-7><0-7> - Set the cos value and
the cos mask for a packet. <0x0600-0xFFFF> - Set the EtherType of the
packet. Shutdown – Disable the Ethernet interface. vlan <1-4094> - Specify the VLAN ID of the
packet. any – Any MAC address. Related Syntax: l
<config-mac-acl >#permit <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
cos <0-7><0-7> l
<config-mac-acl >#permit <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#permit <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl >#permit <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
vlan <1-4094> l
<config-mac-acl >#permit <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
vlan <1-4094>cos <0-7><0-7> l
<config-mac-acl >#permit <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
vlan <1-4094>cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl >#permit <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
vlan <1-4094>ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7> l <config-mac-acl >#permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> l <config-mac-acl >#permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> cos <0-7><0-7> l <config-mac-acl >#permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> cos <0-7><0-7>ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl
>#permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094>
ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> |
|
|
Use the “sequence” command to deny or permit the ACL. <1-2147483647> - Enter the sequence index ACE.
The sequence represents the priority of the ACE in the ACL. <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
>- Specify the source and destination MAC addresses and subnet masks. cos <0-7><0-7> - Set the cos
value and the cos mask for a packet. <0x0600-0xFFFF> - Set the EtherType
of the packet. Shutdown – Disable the Ethernet
interface. vlan <1-4094> - Specify the VLAN ID
of the packet. any – Any MAC address. Related
Syntax: l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7> l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>
ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>
ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> shutdown l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>
shutdown l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF>
shutdown l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> shutdown l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7> l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>
ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>
ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> shutdown l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F
><A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7>
shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any cos <0-7><0-7> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any cos <0-7><0-7> shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any vlan <1-4094> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any vlan <1-4094> cos <0-7><0-7> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any vlan <1-4094> cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any vlan <1-4094> cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any vlan <1-4094> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any vlan <1-4094> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> shutdown l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>deny any any vlan <1-4094> shutdown l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7> l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype
<0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> cos
<0-7><0-7> l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> cos
<0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F>
<A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> ethtype
<0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> cos <0-7><0-7> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any <A:B:C:D:E:F>/<A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any any cos <0-7><0-7> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any any cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any any ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any any vlan <1-4094> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any any vlan <1-4094> cos <0-7><0-7> l <config-mac-acl >#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any any vlan <1-4094> cos <0-7><0-7> ethtype <0x0600-0xFFFF> l
<config-mac-acl
>#sequence <1-2147483647>permit any any vlan <1-4094> ethtype
<0x0600-0xFFFF> |
|
|
mac
address-table aging-time <10-630> |
Set the aging time for an entry remains
in the MAC address table. address-table static - Add a static
address to the MAC address table to drop the packets with the specified
source or destination MAC address. <10-630> - Unit is second. Default
is 300. static <A:B:C:D:E:F> - Enter the MAC address. vlan
<1-4094> - Specify
the VLAN ID of the packet. GigabitEthernet <1-28> - Specify a
physical port. LAG <1-8> -
Specify a LAG port. Related
Syntax: l <config># mac address-table aging-time <10-630> l <config># mac address-table static <A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> drop l <config># mac address-table static <A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> l
<config># mac
address-table static <A:B:C:D:E:F> vlan <1-4094> interfaces LAG
<1-8> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# mac acl test_CA G2100(config-mac-acl)# deny 00:50:00: G2100(config-mac-acl)# deny any 00:50:00: G2100(config-mac-acl)# deny any G2100(config)# mac address-table static
00:50:07:12:ff:aa vlan 300 drop |
Telnet Command: mail alert
Use this command to configure mail
alert for various conditions.
Syntax Items
mailalert active
mailalert auth
mailalert devicecheck
mailalert encry
mailalert interval
mailalert ipconfilict
mailalert password
mailalert port
mailalert portlink
mailalert portspeed
mailalert receiver
mailalert sender
mailalert server
mailalert sysrestart
mailalert throughputcheck
mailalert username
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
mailalert
active |
<disable/enable>
- Enable or disable the function of
mail alert. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert
active <disable/enable> |
|
mailalert
auth |
<disable/enable>
- Enable or disable the function of
SMTP server authentication. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert auth <disable/enable> |
|
mailalert
devicecheck |
<disable/enable> -
Enable or disable the function of sending a mail alert when encountering a
device check error. Related Syntax: l
<config># mailalert devicecheck
<disable/enable> |
|
mailalert
encry |
Specify the
encryption type for mail alert. <disable/ssltls/starttls>
- Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert
encry <disable/ ssltls/starttls> |
|
mailalert
interval |
Set the
transmission interval for the mail alert. <1-60> -
Unit is second. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert
interval <1-60> |
|
mailalert
ipconflict |
<disable/enable>
- Enable or disable the function of
sending a mail alert if encountering the IP conflict. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert ipconflict
<disable/enable> |
|
mailalert
password |
<PASSWORD>
- Enter the password for SMTP server authentication. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert password <PASSWORD> |
|
mailalert
port |
<0-65535>-
Enter a port number. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert port <0-65535> |
|
mailalert
portlink |
<disable/enable>
- Enable or disable the function of
sending an alert when the port lnik status changes. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert portlink
<disable/enable> |
|
mailalert
portspeed |
<disable/enable>
- Enable or disable the function of
sending an alert when the port link speed changes. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert
portspeed <disable/enable> |
|
mailalert
receiver |
Specify an
address for receiving the alart mail. <ADDRESS>
- Enter the email address of the receiver. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert receiver <ADDRESS> |
|
mailalert
sender |
Specify an
address which sends out the alert mail. <ADDRESS>
- Enter the email address of the sender. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert sender <ADDRESS> |
|
mailalert
server |
Set the IP
address of the server. <ADDRESS>
- Enter the IP address of the SMTP server. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert
server <ADDRESS> |
|
mailalert
sysrestart |
<disable/enable>
-Enable or disable the function of
sending a mail alert when the system restarts. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert sysrestart
<disable/enable> |
|
mailalert
throughputcheck |
<disable/enable> -
Enable or disable the function of sending a mail alert when reaching the
throughput threshold. Related Syntax: l
<config># mailalert throughputcheck
<disable/enable> |
|
mailalert
username |
<NAEM> -
Enter the username authenticated by STMP server. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mailalert username <NAME> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# mailalert receiver
[email protected] |
Telnet Command: management
Use this command to create a
management access list and set configuration mode.
Syntax Items
management access-list
management access-class
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
management access-list |
<NAME> - Enter the name of the access list. To configure detailed settings, enter the name of ACL to access into next level. <config>#management access-list <NAME> Then, available sub-commands are: <config-macl>#deny <config-macl>#do <config-macl>#end <config-macl>#exit <config-macl>#permit <config-macl>#sequence |
|
Use the “deny” command to add deny rules for the management access list: GigabitEthernet <1-28> - Specify a physical port. LAG <1-8> - Specify a LAG port. service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> - Specify the servcie type. ip <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> - Specify the source IP address with mask for the packets. ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> - Specify the source IPv6 address and prefix length of the packet. Related Syntax: l <config-macl>#deny interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#deny interfaces LAG <1-8> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#deny ip <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#deny ip <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> interfaces LAG <1-8> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> interfaces LAG <1-8> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> |
|
|
Use the “do” command to run execution command in current mode. <SEQUENCE> - Related Syntax: l <config-macl>#do <SEQUENCE> |
|
|
Use the “end” command to finish current mode. Any changes in current mode will be saved. Related Syntax: l <config-macl>#end |
|
|
Use the “exit” command to close the current CLI session or return to the previous mode without saving the settings. Related Syntax: l <config-macl>#exit |
|
|
Use the “no sequence” command to delete any entry in management ACL. <1-65535>- Specify an index number of the ACL. Related Syntax: l <config-macl>#no sequence <1-65535> |
|
|
Use the “permit” command to add permit rules which bypass the packets meet the rule. GigabitEthernet <1-28> - Specify a physical port. LAG <1-8> - Specify a LAG port. service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> - Specify the servcie type. ip <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> - Specify the source IP address with mask for the packets. ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> - Specify the source IPv6 address and prefix length of the packet. Related Syntax: l <config-macl>#permit interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#permit interfaces LAG <1-8> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#permit ip <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#permit ip <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> interfaces LAG <1-8> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> interfaces LAG <1-8> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> |
|
|
Use the “sequence” command to deny or permit the ACL. <1-65535>- Specify an index number of the ACL. GigabitEthernet <1-28> - Specify a physical port. LAG <1-8> - Specify a LAG port. service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> - Specify the servcie type. ip <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> - Specify the source IP address with mask for the packets. ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> - Specify the source IPv6 address and prefix length of the packet. Related Syntax: l <config-macl>#sequence <1-65535>deny interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#sequence <1-65535>deny interfaces LAG <1-8> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#sequence <1-65535>deny ip <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#sequence <1-65535>deny ip <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> interfaces LAG <1-8> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#sequence <1-65535>deny ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l
<config-macl>#sequence <1-65535>deny ipv6
<X:X::X:X>/<0-128> interfaces LAG <1-8> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#sequence <1-65535> permit interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#sequence <1-65535> permit interfaces LAG <1-8> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#sequence <1-65535> permit ip <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#sequence <1-65535> permit t ip <A.B.C.D>/<A.B.C.D> interfaces LAG <1-8> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#sequence <1-65535> permit ipv6 <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-28> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> l <config-macl>#sequence <1-65535> permit <X:X::X:X>/<0-128> interfaces LAG <1-8> service <all/http/https/snmp/ssh/telnet> |
|
|
management access-class |
Specify an ACL as active access-list. <NAME> - Enter the name of the access list. Related Syntax: l <config># management access-class <NAME> |
Example
|
G2100#
configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)#
management access-list CA_ACL G2100(config-macl)#
deny ip 192.168.2.56/255.255.255.0 interfaces gigabitethernet 3 service
telnet G2100(config-macl)# G2100(config-macl)# deny ipv6
00:50:: |
Telnet Command: management-vlan
Use this command to set VLAN ID
for management VLAN.
Syntax Items
management-vlan vlan
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
management-vlan vlan |
Set the management VLAN ID. <1-4094>- Specify the VLAN ID
number of management VLAN. Related
Syntax: l
<config># management-vlan vlan <1-4094> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# management-vlan vlan 200 VLAN 200: VLAN does not exist G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: mirror
Use this command to set the source
/ destination interface of a port mirror session.
Syntax Items
mirror session
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
mirror session |
Set the destination interface of a port mirror session. <1-4> - Specify the mirror session ID number. GigabitEthernet <1-10> - Specify a physical port. allow-ingress – Enable the ingress traffic forwarding. <both/rx/tx> - Specify the mirror direction, TX only, RX only or TX and RX. Related Syntax: l <config># mirror session <1-4> destination interface GigabitEthernet <1-10> allow-ingress l <config># mirror session <1-4> source interfaces GigabitEthernet <1-10> <both/rx/tx> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# mirror session 3 destination interface
GigabitEthernet 3 allow G2100(config)# G2100(config)# mirror session 3 source interfaces LAG
3 both G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: mvr
Use this command to enable MVR
function and configure related settings.
Syntax Items
mvr
mvr group
mvr mode
mvr query-time
mvr vlan
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
mvr |
Enable MVR function. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mvr |
|
mvr
group |
Set MVR group address. <A.B.C.D> - Enter an IP address. <1-128> - Specify a number for
contiguous series of IPv4 multicast address. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mvr group
<A.B.C.D><1-128> |
|
mvr
mode |
Set MVR mode as compatible or dynamic. <compatible> - The switch does not
support IGMP dynamic joins on the source ports. <dynamic> - The switch supports MVR
membership on the source ports. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mvr mode <compatible/dynamic> |
|
mvr
query-time |
Set query response time for MVR. <1-10> - Specify the response time
(second). Related
Syntax: l
<config># mvr query-time <1-10> |
|
mvr
vlan |
Set a VLAN ID for MVR. <1-4094> - Specify the existed
static VLAN ID. Related
Syntax: l
<config># mvr vlan <1-4094> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# mvr group 192.168.2.33 The operation will delete the MVR VLAN groups include
static MVR groups.Continue ? [yes/no]:y Input Parameter Error G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: no
Use this command to disable
specific command.
Syntax Items
no <command>
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# no port-security G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: openvpn
Use this command to enable/disable
the OpenVPN tunnel.
Syntax Items
openvpn enable
openvpn disable
openvpn
filename
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
enable |
Enable the OpenVPN tunnel. |
|
disable |
Disable the OpenVPN tunnel. |
|
filename |
<NAME> - Define a name for OpenVPN configuration. Related Syntax: l
<config># openvpn filename <NAME> |
Telnet Command: port-security
Use this command to enable the
function of port security.
Syntax Items
port-security
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# port-security G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: qos
Use this command to configure QoS
settings.
Syntax Items
qos
qos map
qos queue
qos trust
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
qos |
Enable the quality of service based on
basic trust type to assign the queue for packets. Related
Syntax: l
<config># qos |
|
qos map
|
map cos-queue - Set the CoS to queue map. map dscp-queue - Set the DSCP to queue
map. map precedence-queue - Set the IP
Precedence to queue map. map queue-cos - Modify the queue to CoS map. map queue-dscp - Modify the queue to DSCP map. map queue-precedence - Modify the queue to IP precedence map. <1-8> - Specify the queue number
for the following CoS values mapped. <1-8> - Specify the queue number to
which the DSCP value shall correspond. <1-8> - Specify the queue number to
which the IP precedence value shall correspond. <0-7> - Enter the cos value to
which the queue ID shall correspond. <0-7> - Enter the DSCP value to
which the queue ID shall correspond. <0-7> - Enter the IP precedence
value to which the queue ID shall correspond. Related
Syntax: l <config># qos map cos-queue SEQUENCE to <1-8> l <config># qos map dscp-queue SEQUENCE to <1-8> l <config># qos map precedence-queue SEQUENCE to <1-8> l <config># qos map queue-cos SEQUENCE to <0-7> l <config># qos map queue-dscp SEQUENCE to <0-7> l
<config># qos map queue-precedence SEQUENCE to
<0-7> |
|
qos
queue |
queue strict-priority-num - Set the
number of strict priority queue. queue weight SEQUENCE - Set the number of
non-strict priority queue. <0-8> - Specify the queue number. <weight1-weight8> <1-127> -
Specify a number (1~127) representing queue weight value. Related
Syntax: l <config># qos queue strict-priority-num <0-8> l
<config># qos queue weight SEQUENCE
<weight1 – weight8> <1-127> |
|
qos
trust |
Set the trust type, cos, for the device
to judge the appropriate queue of the packets. Related
Syntax: l
<config># qos trust <cos/cos-dscp/
dscp/ip-precedence> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# qos map cos-queue SEQUENCE to 3 G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: radius
Use this command to configure
settings for RADIUS server.
Syntax Items
radius default-config
radius host
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
radius default-config |
Key <RADIUSKEY> - Specify key
string for RADIUS server. Retransmit <1-10> - Specify the
retransmit times (from 1 to 10) for RADIUS server. Timeout <1-30> - Specify the time
out value (from 1 to 30) for RADIUS server. Related
Syntax: l <config># radius default-config key <RADIUSKEY> l <config># radius default-config key <RADIUSKEY> retransmit <1-10> l <config># radius default-config key <RADIUSKEY> retransmit <1-10> timeout <1-30> l <config># radius default-config retransmit <1-10> l <config># radius default-config retransmit <1-10> timeout <1-30> l
<config># radius default-config
timeout <1-30> |
|
radius host |
host
<HOSTNAME> - Specify a domain name or IP address for RADIUS server
host. auth-port
<0~65535> - Speicfy a UDP port number for RADIUS server. key
<RADIUSKEY> - Specify
key string for RADIUS server. priority
<0~65535> - Specify the priority for RADIUS server. retransmit
<1-10> - Specify
the retransmit times (from 1 to 10) for RADIUS server. timeout
<1-30> - Specify
the time out value (from 1 to 30) for RADIUS server. type <802.1x
/ all / login> - Choose the usage type for 802.1X authentication, or
login, or both 802.1X authentication and login of RADIUS type. Related
Syntax: l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> auth-port <0~65535> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> auth-port <0~65535> key <RADIUSKEY> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> auth-port <0~65535> key <RADIUSKEY> priority <0~65535> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> auth-port <0~65535> key <RADIUSKEY> priority <0~65535> retransmit <1-10> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> auth-port <0~65535> key <RADIUSKEY> priority <0~65535> retransmit <1-10> timeout <1-30> type <802.1x / all / login> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> key <RADIUSKEY> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> key <RADIUSKEY> priority <0~65535> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> key <RADIUSKEY> priority <0~65535> retransmit <1-10> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> key <RADIUSKEY> priority <0~65535> retransmit <1-10> timeout <1-30> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> key <RADIUSKEY> priority <0~65535> retransmit <1-10> timeout <1-30> type <802.1x / all / login> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> priority <0~65535> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> priority <0~65535> retransmit <1-10> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> priority <0~65535> retransmit <1-10> timeout <1-30> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> priority <0~65535> retransmit <1-10> timeout <1-30> type <802.1x / all / login> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> retransmit <1-10> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> retransmit <1-10> timeout <1-30> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> retransmit <1-10> timeout <1-30> type <802.1x / all / login> l <config># radius host <HOSTNAME> timeout <1-30> l
<config># radius host <HOSTNAME> timeout
<1-30> type <802.1x / all / login> l
<config># radius host
<HOSTNAME> type <802.1x / all / login> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# radius default-config key 123456789
retransmit 3 timeout 10 G2100(config)# radius host radius auth-port 3000 |
Telnet Command: schedule
Use this command to set schedule.
Syntax Items
schedule index
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
schedule index |
Specify an index number for configuring
detailed settings of a schedule profile. <1-15> - Enter a number to select a
schedule profile. <DESCRIPTION> - Give a brief
description for such profile. cycle-days -
The action applied with the schedule will take place every few days. monthly-date - The action applied with the schedule will take place in specified
day within a month. once - The action applied with the
schedule will take place for one time. weekdays - The action applied with the
schedule will take place on a certain day within a week. <1-31> -
Enter a number to make action repeat. <apr / aug /
dec / feb /jan / jul / jun /jul / mar / may / nov / oct / sep > - Represent month of April, August,
December, February, January, July, June, March, May, November, October, and
September. <sun /mon
/tue /wed / thu / fri / sat> - Represent
Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday and Saturday. <1-31> -
Enter a number as the start date within a month. <2000-2035>
- Enter the number as the year of start date. <HH:MM> - Enter the hours and the miniutes. <on/off>
- Enable (on) or disable (off) the action applied with such profile. Related
Syntax: l <config># schedule index <1-15> description <DESCRIPTION> l <config># schedule index <1-15> how-often cycle-days <1-31> start-date <apr / aug / dec / feb /jan / jul / jun / mar / may / nov / oct / sep > <1-31> <2000-2035> start-time <HH:MM> duration <HH:MM> action <on/off> l <config># schedule index <1-15> how-often monthly-date <1-31> start-date <apr / aug / dec / feb /jan / jul / jun / mar / may / nov / oct / sep > <1-31> <2000-2035> start-time <HH:MM> duration <HH:MM> action <on/off> l <config># schedule index <1-15> how-often once start-date<apr / aug / dec / feb /jan / jul / jun / mar / may / nov / oct / sep > <1-31> <2000-2035> start-time <HH:MM> duration <HH:MM> action <on/off> l
<config># schedule
index <1-15> how-often weekdays <sun /mon /tue /wed / thu / fri /
sat> start-date <apr / aug / dec / feb /jan / jul / jun / mar / may /
nov / oct / sep > <1-31> <2000-2035> start-time <HH:MM>
duration <HH:MM> action <on/off> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# schedule index 1 how-often cycle-days
3 start-date jan 1 2019 start-time 08:01 duraton 17:30 action on G2100(config)# schedule index 2 how-often weekdays sun start-date
may 11 2019 start-time 02:10 duration 12:10 action on G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: snmp
Use this command to define SNMP
community.
Syntax Items
snmp community
snmp engineid
snmp group
snmp host
snmp trap
snmp user
snmp view
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
snmp community |
snmp community - Set community name for SNMP v1 and v2,
and access group name. Available
parameters for SNMP community: <NAME> after community - Enter a
string (maximum length: 20 characters) as community name. <NAME> after group - Enter a string
(maximum length: 30 characters) as access group. ro - Set the community as read only. rw - Set the community as read and write. Related Syntax: l <config># snmp community <NAME> group <NAME> l <config># snmp community <NAME> ro l <config># snmp community <NAME> rw l <config># snmp community <NAME> view <NAME> ro l
<config># snmp community
<NAME> view <NAME> rw |
|
snmp engineid |
snmp engineid -
Set the remote
host for SNMP engine. default - Reset to default setting of
engine ID for SNMP server. <ENGINEID> - Such number must be 10
~ 64 hexadecimal. <A.B.C.D>
- Enter the IP address of the remote SNMP server. <HOSTNAME> - Enter the host name of
the remote SNMP server. <X:X::X:X> - Enter the IPv6 address
for remote SNMP server. Related Syntax: l <config># snmp engineid <ENGINEID> l <config># snmp engineid default l <config># snmp engineid remote <A.B.C.D> <ENGINEID> l <config># snmp engineid remote <HOSTNAME> <ENGINEID> l
<config># snmp engineid remote
<X:X::X:X><ENGINEID> |
|
snmp group |
snmp group - Set the SNMP group. <NAME> - Specify the name of SNMMP
group. version <1/ <auth/noauth/priv>
- Specify the packet authentication mode. “auth” means to perform packet
authentication without encryption. It is applicable for SNMPv3 only. “noauth”
means no packet authentication performed. “priv” means to perform packet
authentication with encryption and also it is applicable for SNMPv3 only. read-view
<NAME> - Set the view name to enable agent configuration. notify-view
<NAME> - Set the view name to send only trap included in SNMP view for
notification. write-view
<NAME> - Set the view name to enable viewing. Related Syntax: l
<config># snmp group
<NAME> version <1/ l
<config># snmp group
<NAME> version <1/ l
<config># snmp group
<NAME> version <1/ |
|
snmp host |
snmp host - Set a host to receive SNMP notifications. <A.B.C.D>
- Enter the IPv4/IPv6 address or host name of the receipt. version <1/ <NAME> -
Set the community name sent with the notification. udp-port <1-65535> - Set the UDP port number. timeout
<1-300> - Set the timeout of V retries
<1-255> - Enter the retry counter of V Related Syntax: Set a
host to receive SNMP notifications. l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> <NAME> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> <NAME> timeout <1-300> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> retries <1-255> l
<config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> <NAME>
udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> |
|
Set a host to
receive SNMP notifications. Notification type is informs. l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> informs <NAME> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> informs <NAME> timeout <1-300> l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> informs <NAME> timeout <1-300> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> informs <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> informs <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> informs <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> informs <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> retries <1-255> l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> informs version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> informs version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> informs version <1/ l
<config># snmp host <A.B.C.D>
informs version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> informs version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> informs version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> informs version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> informs version <1/ |
|
|
Set a host to
receive SNMP notifications. Notification type is traps. l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> traps <NAME> l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> traps <NAME> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> traps <NAME> timeout <1-300> l <config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> traps <NAME> timeout <1-300> retries <1-255> l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> traps version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> traps version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> traps version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> traps version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> traps version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> traps version <1/ |
|
|
l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> version <1/ l
<config># snmp host <A.B.C.D> version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<A.B.C.D> version <1/ l
<config>#snmp host
<A.B.C.D> version <1/ |
|
|
l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
<NAME> l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
<NAME> retries <1-255> l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
<NAME> timeout <1-300> l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
<NAME> timeout <1-300> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
<NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> retries
<1-255> |
|
|
l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
informs <NAME> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME informs <NAME> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME informs <NAME> timeout <1-300> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME informs <NAME> retries <1-255> timeout <1-300> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME informs <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME informs <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME informs <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
informs <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> retries
<1-255> |
|
|
l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
traps <NAME> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME traps <NAME> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME traps <NAME> timeout <1-300> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME traps <NAME> timeout <1-300> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME traps <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> l <config># snmp host HOSTNAME traps <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> retries <1-255> l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
traps <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
traps <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> retries
<1-255> l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
traps version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
traps version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
traps version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
traps version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME traps
version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
traps version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
traps version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
version <1/ l
<config># snmp host HOSTNAME
version <1/ |
|
|
l
<config># snmp host
<X:X::X:X> <NAME> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> <NAME> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> <NAME> retries <1-255> timeout <1-300> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> <NAME> retries <1-255> timeout <1-300> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> informs <NAME> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> informs <NAME> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> informs <NAME> timeout <1-300> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X>informs <NAME> retries <1-255> timeout <1-300> retries <1-255> l
<config># snmp host
<X:X::X:X> informs <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> l
<config># snmp host <X:X::X:X>
informs <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> retries <1-255> l
<config># snmp host
<X:X::X:X> informs <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout
<1-300> l
<config># snmp host
<X:X::X:X> informs <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout
<1-300> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> traps <NAME> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> traps <NAME> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> traps <NAME> timeout <1-300> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> traps <NAME> timeout <1-300> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> traps <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> traps <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> retries <1-255> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> traps <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> l <config># snmp host <X:X::X:X> traps <NAME> udp-port <1-65535> timeout <1-300> retries <1-255> l
<config># snmp host
<X:X::X:X> version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<X:X::X:X> version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<X:X::X:X> version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<X:X::X:X> version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<X:X::X:X> version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<X:X::X:X> version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<X:X::X:X> version <1/ l
<config># snmp host
<X:X::X:X> version <1/ |
|
|
snmp trap |
snmp trap - Send the SNMP traps. auth – Enable
the SNMP authentication failure trap. cold-start –
Enable the SNMP cold startup failure trap. linkUpDown –
Enable the SNMP link up and down failure trap. wort-security –
Enable the SNMP port security trap. Warm-start –
Enable the SNMP warm startup failure trap. Related Syntax: l
<config># snmp trap <auth /
cold-start / linkUpDown / port-security / warm-start> |
|
snmp user |
snmp user - Set
SNMP user account. <username> - Specify a name of SNMP user. <groupNAME> - Sepcify a name of SNMP group. auth <md5/sha> - Specify the authentication mode, md5 or sha. <AUTHPASSWD> - Enter the password for the md5/sha mode. Pri <PRIVPASSWD> - Enter a password as a privacy key. Related Syntax: l <config># snmp user <sername> <groupNAME> l <config># snmp user <sername> <groupNAME> auth <md5/sha> <AUTHPASSWD> l
<config># snmp user
<sername> <groupNAME> auth <md5/sha> <AUTHPASSWD>
priv <PRIVPASSWD> |
|
snmp view |
snmp view - Set the
SNMP view. <NAME> - Enter the SNMP view name. Subtree <OID> - Specify the ASN.1 subtree object identifier
(OID). oid-mask <mask/all> - Speicfy the OID mask, or use all for
all masks. viewtype <exluded/included> - Let the selected MIBs
include or exclude in the SNMP view. Related Syntax: l
<config># snmp view <NAME>
subtree <OID> oid-mask <mask> viewtype <excluded/included> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# snmp engineid remote 192.168.2.38
00036D001188 G2100(config)# snmp engineid remote 00:50::16:88
00036D002288 G2100(config)# snmp host 192.168.2.89 CAR_community
udp-port 1500 timeout 200 G2100(config)# snmp host 192.168.2.88 informs version
G2100(config)# snmp host 192.168.2.88 traps version G2100(config)# snmp host 192.168.2.88 version G2100(config)# snmp host HOSTNAME CAR_host
udp-port 3000 timeout 60 retries G2100(config)# snmp host HOSTNAME informs
HA_informs udp-port 3000 timeout 60 retries 2 G2100(config)# snmp host HOSTNAME version G2100(config)# snmp user CA_user_1 CA_group_1
auth md5 CA12345678 priv PR12345678 G2100(config)# snmp view CAR_community subtree 10
oid-mask 9 viewtype included G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: sntp
Use this command to configure
settings for remote SNTP server.
Syntax Items
sntp host
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
sntp host |
Set the remote SNTP server by specifying
IP address or hostname. <HOSTNAME> - Enter the IP address
or hostname of SNTP server. <1-65535> - Specify the port number
for the SNTP server. Related Syntax: l <config># sntp host <HOSTNAME> l
<config># sntp host
<HOSTNAME>> port <1-65535> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# sntp host KEY1245 port 3000 G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: spanning-tree
Use this command to configure
settings for spanning-tree.
Syntax Items
spanning-tree
spanning-tree bpdu
spanning-tree forward-delay
spanning-tree hello-time
spanning-tree max-hops
spanning-tree maximum-age
spanning-tree mode
spanning-tree mst
spanning-tree pathcost
spanning-tree priority
spanning-tree tx-hold-count
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
spanning-tree |
Enable the function of spanning-tree. Related Syntax: l
<config># spanning-tree |
|
spanning-tree
bpdu |
Filter/flood the BPDU packets. <filtering> - Packets will be filtered
when STP is disabled on specified interface. <flooding> - Packets will be
flooded to all interfaces with STP disabled and flooding mode. Related Syntax: l
<config># spanning-tree bpdu<filtering/flooding> |
|
spanning-tree
forward-delay |
Set the STP forward delay time. <4-30> - Default value is 15
(seconds). Related Syntax: l
<config># spanning-tree forward-delay <4-30> |
|
spanning-tree
hello-time |
Set the hello time interval to broadcast
the message to other bridges. <1-10> - Default value is 2
(seconds). Related Syntax: l
<config># spanning-tree hello-time <1-10> |
|
spanning-tree
max-hops |
Set the number of hops for BPDI packets
to be forwarded in the MSTP region. <1-40> - Default value is 20
(seconds). Related Syntax: l
<config># spanning-tree max-hops
<1-40> |
|
spanning-tree
maximum-age |
Set the time interval for VigorSwitch to
wait without receiving the configuration message. <6-40> - Default value is 20
(seconds). Related Syntax: l
<config># spanning-tree
maximum-age <6-40> |
|
spanning-tree
mode |
<mstp/rstp/stp> - Specify the
operation mode for spanning tree, such as multiple spanning tree (MSTP),
rapid spanning tree (RSTP) or spanning tree (STP). Related Syntax: l
<config># spanning-tree mode
<mstp/rstp/stp> |
|
spanning-tree
mst |
spanning-tree
mst -
Configure port priority settings for MST. <0-15> - Specify the instance ID. <0-61440> - Set the priority for
the specified instance ID. Related Syntax: l
<config># spanning-tree mst <0-15>
priority <0-61440> |
|
spanning-tree mst configuration - Access
into the MSTP configuration mode. To configure detailed settings, access into
next level. <config># spanning-tree mst
configuration <config-mst># Then, available sub-commands are: <config-mst>#do <config-mst># end <config-mst># exit <config-mst># instance <config-mst># name <config-mst># no <config-mst># revision do <SEQUENCE> - Enter
the action to be performed. end - End current mode. exit - Exit from current mode. instance
<0-15> vlan <1-4094> - Specify the instance ID number and VLAN ID
number. name
<NAME> - Set a name of MST configuration. no - Set to
default setting. revision
<0-65535> - Set revision level. |
|
|
spanning-tree
pathcost |
Set the path-cost method for spanning
tree. <long/short> - Long means the path
cost ranging from 1 to 200000000; short means the path cost ranging from 1 to
65535. Related Syntax: l
<config># spanning-tree pathcost
method <long/short> |
|
spanning-tree
priority |
Set the priority for the specified
instance ID. <0-61440> - The number must be
multiple of 4096. Related Syntax: l
<config># spanning-tree priority
<0-61440> |
|
spanning-tree
tx-hold-count |
Set the maximum number of packets
transmission per second. <1-10> - Valid range is from 1 to
10. Related Syntax: l
<config># spanning-tree
tx-hold-count <1-10> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# spanning-tree forward-delay 20 G2100(config)# G2100(config)# spanning-tree maximum-age 38 G2100(config)# G2100(config)# spanning-tree tx-hold-count 3 G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: start-up
Use this command to restart ICP
status after rebooting VigorSwitch.
Syntax Items
start-up icp
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
start-up icp |
Related Syntax: l
<config># start-up icp enable |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# start-up icp enable G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: storm-control
Use this command to configure
settings for Storm Control.
Syntax Items
storm-control ifg exclude
storm-control ifg include
storm-control unit bps
storm-control unit pps
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
storm-control ifg exclude |
Exclude the preamble and IFG (inter frame
gap) into the calculating. Related Syntax: l
<config># storm-control ifg
exclude |
|
storm-control ifg include |
Include the preamble and IFG (inter frame
gap) into the calculating. Related Syntax: l
<config># storm-control ifg
include |
|
storm-control unit bps |
Change the unit of calculating method for
storm-control. bps – Calculate the storm control rate by
octet-based. Related Syntax: l
<config># storm-control unit bps |
|
storm-control unit pps |
Change the unit of calculating method for
storm-control. pps – Calculate the storm control rate by
packet-based. Related Syntax: l
<config># storm-control unit pps |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# storm-control ifg exclude G2100(config)# G2100(config)# storm-control unit bps G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: surveillance-vlan
Use this command to configure
settings for surveillance-VLAN.
Syntax Items
surveillance-vlan
surveillance-vlan aging-time
surveillance-vlan cos
surveillance-vlan oui-table
surveillance-vlan vlan
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
surveillance-vlan |
Enable the function of surveillance VLAN
on VigorSwitch. Related Syntax: l
<config># surveillance-vlan |
|
surveillance-vlan
aging-time |
Set the aging time for surveillance VLAN. <30-65536> - Enter a value as aging
time. Related Syntax: l
<config># surveillance-vlan
aging-time <30-65536> |
|
surveillance-vlan
cos |
Set the class of service (0~7) for
surveillance VLAN. <0-7>- Enter a number. Related Syntax: l
<config># surveillance-vlan cos
<0-7> remark |
|
surveillance-vlan oui-table |
Enable OUI surveillance VLAN
configuration for specified interface. <A:B:C> - Enter the OUI address
(e.g., 00:50:12). <DESCRIPTION> - Enter a string to
briefly explain the surveillance VLAN. Related Syntax: l
<config># surveillance-vlan oui-table <A:B:C> <DESCRIPTION> |
|
surveillance-vlan
vlan |
Specify a VLAN profile as surveillance
VLAN. <2-4094> - Specify the surveillance
VLAN ID. Related Syntax: l
<config># surveillance-vlan vlan
<2-4094> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# G2100(config)# surveillance-vlan aging-time 60 G2100(config)# G2100(config)# surveillance-vlan oui-table
00:50:12 fortestonly G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: system
Use this command to modify the
contact information of VigorSwitch.
Syntax Items
system contact
system location
system name
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
system contact
|
<CONTACT> - Enter a string (maximum
length: 256 characters). Related Syntax: l
<config># system contact
<CONTACT> |
|
system
location |
<LOCATION> - Specify the location
of the host. Related Syntax: l
<config># system location
<LOCATION> |
|
system
name |
<NAME> - Change the name of the
system. The default name is “G Related Syntax: l
<config># system name
<NAME> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# system contact callMIS G2100(config)# G2100(config)# system location DrayTek G2100(config)# system name UPDATEFRIM UPDATEFRIM(config)# |
Telnet Command: tacacs
Use this command to configure
TACACS+ server.
Syntax Items
tacacs default-config
tacacs host
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
tacacs
default-config |
Set the default parameters for the
TACACS+ server. Modify the default parameters of server
key and timeout setting for the TACACS+ server. <TACPLUSKEY> - Enter a string as
the TACACS+ server key. <1-30> - Enter a value as the
TACACS+ server timeout. Related Syntax: l <config># tacacs default-config l <config># tacacs default-config key <TACPLUSKEY> l
<config># tacacs default-config
key <TACPLUSKEY> timeout <1-30> |
|
tacacs host |
Set host name for the TACACS+ server or
set host name, server key and priority for the TACACS+ server. <HOSTNAME> - Enter the host name of
the TACACS+ server. <TACPLUSKEY> - Enter a string as
the TACACS+ server key. <0-65535> - Enter a value as server
priority in server group. <1-30> - Enter a timeout setting. Related Syntax: l <config># tacacs host <HOSTNAME> l <config># tacacs host <HOSTNAME> key <TACPLUSKEY> l <config># tacacs host <HOSTNAME> key <TACPLUSKEY> priority <0-65535> l
<config># tacacs host
<HOSTNAME> key <TACPLUSKEY> priority <0-65535> timeout
<1-30> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# tacacs default-config key tce00056
timeout 25 G2100(config)# G2100(config)# tacacs host carrie02 key TA012345
priority 3000 timeout 10 G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: tr069
Use this command to configure
parameter settings of TR-069.
Syntax Items
tr069 acsPwd
tr069 acsUsername
tr069 acsurl
tr069 cpeEnable
tr069 cpePwd
tr069 cpeUsername
tr069 cpeport
tr069 healthlinkstatus
tr069 healthpoewarning
tr069 healthspeedstatus
tr069 periodicInfo
tr069 periodicTime Time
tr069 ssl
tr069 stun
tr069 stunMAXkeepalive
tr069 stunMINkeepalive
tr069 stunaddr
tr069
stunport
tr069 tls
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
tr069 acsPwd |
<PASSWORD> - Enter the password
used for registering to VigorACS server. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 acsPwd<PASSWORD> |
|
tr069 acsUsername |
<NAME> - Enter the username used
for registering to VigorACS server. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 acsUsername<NAME> |
|
tr069 acsurl |
<ADDRESS> - Enter the URL for
VigorACS server. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 acsurl <ADDRESS> |
|
tr069 cpeEnable |
<disable/enable> - Enter Enable for
VigorACS controlling such CPE through the Internet. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 cpeEnable <disable/enable> |
|
tr069 cpePwd |
<PASSWORD> - Enter the password
that VigorACS server can use it to authenticate and control the CPE device. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 cpePwd <PASSWORD> |
|
tr069 cpeUsername |
<NAME> - Enter the username that
VigorACS server can use it to authenticate and control the CPE device. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 cpeUsername <NAME> |
|
tr069 cpeport |
<0-65535> - Enter the port number
for CPE. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 cpeport <0-65535> |
|
tr069 healthlinkstatus |
Perform the health check for the link
status of specified interface(s). <PORTLIST> - Specify the interface,
such as GE1, GE3-GE5 and so on. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 healthlinkstatus
<PORTLIST> |
|
tr069 healthpoewarning |
Perform the health check for PoE port
warning status. <PORTLIST> - Specify the interface,
such as GE1, GE3-GE5 and so on. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 healthpoewarning <PORTLIST> |
|
tr069 healthspeedstatus |
Perform the health check for link speed
status of specified interface(s). <PORTLIST> - Specify the interface,
such as GE1, GE3-GE5 and so on. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 healthspeedstatus <PORTLIST> |
|
tr069 periodicInfo |
<disable/enable> - Enter Enable to
activate periodic information setting. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 periodicInfo <disable/enable> |
|
tr069 periodicTime TIME |
Update the CPE information to VigorACS
server. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 periodicTime TIME |
|
tr069 ssl |
<disable/enable> - Enter Enable to
enable CPE management protocol with SSL. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 ssl <disable/enable> |
|
tr069 stun |
<disable/enable> - Enter Enable to
enable CPE management protocol with STUN server. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 stun <disable/enable> |
|
tr069 stunMAXkeepalive |
Set the maximum time period for CPE to
send the binding request to VigorACS server. <0-65535> - Enter a number. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 stunMAXkeepalive <0-65535> |
|
tr069 stunMINkeepalive |
Set the minimum time period for CPE to
send the binding request to VigorACS server. <0-65535> - Enter a number. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 stunMINkeepalive
<0-65535> |
|
tr069 stunaddr |
<ADDRESS> - Enter the URL/IP address
of STUN server. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 stunaddr <ADDRESS> |
|
tr069 stunport |
<0-65535> - Set the port number for
STUN server. Related Syntax: l
<config># tr069 stunport <0-65535> |
|
tr069 tls |
<tlsl.2/tls1.3> - Set the TLS version (2 or 3) for VigorSwitch. Related Syntax: l <config># tr069 tls version <tlsl.2/tls1.3> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# tr069 stunaddr 192.168.3.99 G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: udld
Use this command to set the time
interval of UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD) sent message.
Syntax Items
udld
Description
|
Syntax Items |
Description |
|
udld message time |
<1-90> - Specify a time interval
for sending message. Related Syntax: l
<config>#udld message time
<1-90> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# udld message time 35 G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: username
Use this command to add a new user
account or edit an existing user account.
Syntax Items
username
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
username |
privilege - Set a user account with the
privilege of admin, user or customized level. secret - Set a user account with
unencrypted password. secret encrypted - Set a user account
with encrypted password. <WORD> - Enter the name (0~32
characters) of the local user profile. <admin/ user> - Specify the privilege
level to be admin (privilege 15) / user (privilege 1). <PASSWORD> - Enter a string as the
password for the local user. Related Syntax: l <config># username <WORD> privilege <admin/user> secret <PASSWORD> l <config># username <WORD> secret <PASSWORD> l
<config># username <WORD>
secret encrypted <PASSWORD> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# username carrie_1 privilege admin
secret md123456 G2100(config)# G2100(config)# username carrie_1 secret encrypted
ca123456 Old password: ******** G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: vlan
Use this command to configure
detailed settings for VLAN profile.
Before configuring, you have to access into next phase. See the following example:
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# G2100(config)# vlan 3 P1280(config-vlan)# |
Syntax Items
vlan vlan-list
vlan mac-vlan group
vlan protocol-vlan group
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
vlan |
Specify the index number of VLAN profile. To configure detailed settings, access into next
level. <vlan-list> - The available range
is 1 to 4094. <config># vlan 33 <config-vlan># Then, available sub-commands are: <config-vlan>#do <config-vlan>#end <config-vlan>#exit <config-vlan>#name |
|
Use the “do” command to run execution
command in current mode. <SEQUENCE> - Related
Syntax: l
<config-vlan>#do <SEQUENCE> |
|
|
Use the “end” command to finish current
mode. Any changes in current mode will be saved. Related
Syntax: l
<config-vlan>#end |
|
|
Use the “exit” command to close the
current CLI session or return to the previous mode without saving the settings. Related
Syntax: l
<config-macl>#exit |
|
|
Use the “name” command to add a VLAN
profile. <string>
- Enter the name of the VLAN profile. Related
Syntax: l
<config-vlan>#name <string> |
|
|
vlan
mac-vlan group |
Create a
MAC-vlan group. <1-2147483647>
- Specify a group ID. <A:B:C:D:E:F>
- Enter the MAC address to be mapped. <9-48> -
Enter a number representing the subnet mask. Related Syntax: l
<config># vlan mac-vlan group
<1-2147483647> <A:B:C:D:E:F> mask <9-48> |
|
vlan
protocol-vlan group |
Create a
protocol VLAN group with specified protocol type and value. <1-8> -
Enter a number to specify a VLAN group. <Ethernet_ii/ <value> - Enter a value
(0x0600~0xFFFE). Related Syntax: l
<config># vlan protocol-vlan
group <1-8> frame-type <Ethernet_ii/ |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# vlan 3 G2100(config-vlan)# G2100(config-vlan)# name vlan_friends G2100(config-vlan)# … G2100(config)# vlan mac-vlan group 33
00:50:17:22:12:ff mask 10 G2100(config)# vlan group 1 frame-type ethernet_ii protocol-value
0x0600 G2100(config)# |
Telnet Command: voice-vlan
Use this command to enable voice
VLAN and configure settings for voice VLAN.
Syntax Items
voice-vlan aging-time
voice-vlan cos
voice-vlan oui-table
voice-vlan vlan
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
voice-vlan aging-time |
Set the voice VLAN aging timeout
interval. <30-65536>
- The unit is minute. Default is 1440 (minutes). <string>
- Enter the name of the VLAN profile. Related Syntax: l
<config># voice-vlan aging-time
<30-65536> |
|
voice-vlan cos |
Set the voice VLAN cos value and remark
function. Specify the class of service for voice
VLAN. <0-7> - CoS value. Default is 6.
Remark is disabled. remark – L2 user priority is remarked
with the Related Syntax: l
<config># voice-vlan cos
<0-7> remark |
|
voice-vlan oui-table |
Add or remove the selected OUI to/from
the OUI table. In default, there are 8 OUI addresses. <A:B:C> - Enter the OUI address. <DESCRIPTION> - Enter a brief
description for the specified MAC address to the voice VLAN OUI table. Related Syntax: l
<config># voice-vlan cos
<0-7> remark |
|
voice-vlan vlan |
Set the VLAN identifier of the voice
VLAN. <2-4094> - Enter the number of VLAN
ID. Related Syntax: l
<config># voice-vlan vlan <2-4094> |
Example
|
G2100# configure G2100(config)# voice-vlan aging-time 1000 G2100(config)# G2100(config)# voice-vlan oui-table 22:30:ff test_01 G2100(config)# G2100(config)# voice-vlan oui-table 00:01:E2 STAMP G2100(config)# exit G2100# show voice-vlan interfaces gigabitEthernet 1 Voice VLAN Aging : 1000 minutes Voice VLAN CoS : 6 Voice VLAN 1p Remark: disabled OUI table OUI MAC | Description --------------+----------------- 00:E0:BB | 3COM 00:03:6B | Cisco 00:E0:75 | Veritel 00:D0:1E | Pingtel 00:01:E3 | Siemens 00:60:B9 | NEC/Philips 00: 00:09:6E | Avaya 22:30:FF | test_01 00:01:E2 | STAMP Port | State | Port Mode | Cos Mode -------+----------+-------------+----------- gi1
| Disabled |
Auto |
Src G2100# |
Telnet Command: webhook
Use this command to enable or
disable the webhook service.
Syntax Items
webhook active
webhook host
webhook interval
webhook keep
Description
|
Syntax Items |
Description |
|
webhook active |
<enable/disable> - Enable or disable the
webhook application. Related
Syntax: l
<config># webhook active
<enable/disable> |
|
webhook host |
Specify the destination (URL, domain name, IP
address) to receive the data transferred by VigorSwitch. ip
<ADDRESS> - Enter the IP address of the destination. path <PATH> - Enter the path string (part of
the composition of the URL) of the destination. port <number> - Enter a port number. service <http/https> - Specify the protocol
(http or https) of the destination. url <domain name> - Enter the domain name
(e.g., draytek.com) of the destination. Note that it is not necessary to
enter this information if IP address has been set first. Related
Syntax: l <config># webhook host ip <ADDRESS> l <config># webhook host path <PATH> l <config># webhook host port <number> l <config># webhook host service <http/https> l
<config># webhook host url
<domain name> |
|
webhook interval |
<1-60> - Set the transmission interval (unit is
minute). Related Syntax: l
<config># webhook interval
<1-60> |
|
webhook keep |
setings <enable/disable> - Enable or disable
the function of keep webhook settings. Related Syntax: l
<config># webhook keep setings
<enable/disable> |
Example
|
G2100#
configure G2100(config)#
webhook host service https G2100(config)#
webhook host url www.demo.com G2100(config)#
webhook host path Draytek/demo G2100(config)#
webhook host port 443 G2100(config)#
webhook interval 2 |
Use this command to upgrade firmware image, configuration file,
syslog file, language file and security certificate.
Syntax Items
copy flash://
copy tftp://
copy backup-config
copy running-config
copy startup-config
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
copy flash:// |
Related Syntax: l # copy flash:// flash:// l
# copy flash:// tftp:// |
|
copy running-config |
startup-config - Copy the running configuration file to
startup configuration. tftp://- Copy the running configuration file to
remote TFTP server with a filename. <IP address> - Enter the IP address
of TFTP sever. <filename> - Create a name to save
the configuration file. Related Syntax: l # copy running-config backup-config l # copy running-config startup-config l
# copy running-config tftp:// |
|
copy startup-config |
running-config - Copy the startup configuration file to
the running configuration. tftp://- Copy the startup configuration file to
remote TFTP server with a filename. <IP address> - Enter the IP address
of TFTP sever. <filename> - Create a name to save
the configuration file. Related Syntax: l # copy startup-config backup-config l # copy startup-config running-config l
# copy startup-config tftp:// |
|
copy tftp:// |
Backup-config -
Get the backup configuration from specified TFTP server. running-config - Get the running configuration from
specified TFTP server. startup-config - Get the startup configuration from
specified TFTP server. Related Syntax: l # copy tftp:// backup-config l # copy tftp:// flash:// l # copy tftp:// running-config l # copy tftp:// startup-config l
# copy tftp:// tftp:// |
Example
|
G2100# copy running-config
tftp://172.16.3.8/test_carrie.cfg Uploading file. Please wait... Save configuration done. G2100# copy startup-config
tftp://172.16.3.8/test_da.cfg Uploading file. Please wait... Save configuration done. G2100# |
Use this command to delete a file
from the FLASH file system or restore the factory default settings of
VigorSwitch.
Syntax Items
delete backup-config
delete flash://
startup-config
delete startup-config
delete system
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
delete
backup-config |
Delete the backup configuration file in FLASH file system. Related Syntax: l
# delete backup-config |
|
delete
flash://startup-config |
Delete the startup configuration file in FLASH file system. Related Syntax: l
# delete flash://startup-config |
|
delete startup-config |
Restore the factory default settings of
VigorSwitch. Related Syntax: l
# delete startup-config |
|
delete
system |
Delete the firmware image0/image1 stored
in FLASH file system. <image0/image1> - Related Syntax: l
# delete system <image0/image1> |
Example
|
G2100# delet flash://startup-config Delete flash://startup-config [y/n] y Do you want to reload the system to take
effect? [y/n] y … |
All commands used will be divided into EXEC mode and Privileged EXEC mode. This command is to turn off privileged mode command.
Default privilege level is 15 if no privilege level is specified on enable command.
Default privilege level is 1 if no privilege level is specified on
disable command.
Syntax Items
disable
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
disable |
<1-14> - Enter a
number to specify the privilege level. Related Syntax: l
# disable <1-14> |
Example
|
G2100# disable ?
<1-14> Privilege
level
<cr> G2100# disable 3 G2100> |
Use this command to end current mode.
Syntax Items
end
Example
|
G2100(config)# interface GigabitEthernet
3 G2100(config-if)# end G2100# |
Use this command to close current CLI session or return to previous
mode.
Syntax Items
exit
Example
|
G2100(config)# interface GigabitEthernet
3 G2100(config-if)# exit G2100(config)# |
I-2-9 Hardware-Monitor
Configuration
Use this command to execute the hardware fan test.
Syntax Items
hardware-monitor fan-test
Example
|
G2100# hardware-monitor
fan-test G2100# |
I-2-10
Use this command to send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to network hosts.
Syntax Items
ping
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
ping |
<HOSTNAME> - Enter an IPv4/IPv6 address or a domain
name to ping. count <1-999999999> - Specify the number of repetitions of ping
operation. Related Syntax: l
# ping <HOSTNAME> count <1-999999999> |
Example
|
G2100# ping 192.168.1.11 count 3 64 bytes from 192.168.1.11: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64
time=0.0 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.1.11: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64
time=0.0 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.1.11: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64
time=0.0 ms --- 192.168.1.11 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet
loss round-trip min/avg/max = 0.0/0.0/0.0 ms G2100# |
Use this command to perform a cold restart of VigorSwitch.
Syntax Items
reboot
Example
|
G2100# reboot G2100# |
Use this command to renew DHCP Snooping database from backup file.
Syntax Items
renew ip dhcp snooping
database
Example
|
G2100#
renew ip dhcp snooping database G2100# |
I-2-13
Restore-defaults Configuration
Use this command to restore the factory default settings for the
system or for the selected port.
Syntax Items
restore-defaults
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
restore-default |
<1-10>
- Enter the number (1 to 10) of LAN port. <1-8>
- Enter the number of LAG port. Related Syntax: l
# restore-default l
# restore-default interfaces GigabitEthernet
<1-10> l
# restore-default interfaces LAG <1-8> |
Example
|
G2100# restore-defaults interfaces gigabitethernet 3 Interface gi3: restore factory defaults. G2100# G2100# restore-default System: restore factory defaults. Do you want to
reboot now? (y/n)y |
I-2-14 Save Configuration
Use this command to save configuration and activate the settings.
Note that this command has the
same effect as "copy running-config startup-config".
Syntax Items
save
Example
|
G2100# save Success G2100# |
I-2-15 Show
Configuration
After finished the command setting, use this command to display the configuration for all commands.
Syntax Items
show <command>
Example
|
G2100# show
acl utilization Type:
sys
usage: 256 Type:
IPSG
usage: 128 Type:
Auth
usage: 128 Type:
(null) usage:
128 Type:
(null)
usage: 128 G2100# G2100# show
arp Address
HWtype HWaddress
Flags Mask
Iface 192.168.1.9 ether 60:A4: 192.168.1.1 ether 00:1D:AA:6D:D1: G2100# |
I-2-16 SSL
Configuration
Use this command to generate security certificate files such as RSA, DSA.
After entering the command of SSL, follow the onscreen questions to
give the required information.
Syntax Items
ssl
Example
|
G2100# ssl Generating a 1024 bit RSA private key .............................................++++++ ..............................++++++ writing new private key to '/mnt/ssh/ssl_key.pem_tmp' ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that
will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a
Distinguished Name or a D There are quite a few fields but you can leave some
blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:tw State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:hs Locality Name (eg, city) []:hschu Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty
Ltd]:draytek Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:marketing Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name)
[]:draytek Email Address []:[email protected] G2100# |
I-2-17
Terminal Configuration
Use this command to set the maximum line number that the terminal is
able to print.
Syntax Items
terminal
Syntax
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
terminal |
<0-24> - Enter the length value. 0
means no limit. Related Syntax: l
# terminal length <0-24> |
Example
|
G2100# terminal length 15 G2100# show running-config …… |
I-2-18 Traceroute
Configuration
Use this command to execute network trace route diagnostic.
Syntax Items
traceroute
Syntax
Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
traceroute |
<HOSTNAME>- Enter the IP address or
the hostname of the device for VigorSwitch to perform traceroute diagnostic. Related Syntax: l
# traceroute <HOSTNAME> |
Example
|
G2100# traceroute 192.168.1.224 traceroute to 192.168.1.224 (192.168.1.224), 30 hops
max, 40 byte packets 1 192.168.1.224 (192.168.1.224) 0 ms 0 ms 0 ms G2100# |
I-2-19 UDLD Configuration
Use this command
to reset all interfaces disabled by the
UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD) and make data traffic begin passing
through the interfaces again.
Syntax Items
udld
Syntax Description
|
Syntax
Items |
Description |
|
udld |
Enter
the IP address or the hostname of the device for VigorSwitch to perform traceroute diagnostic. Related Syntax: l
# udld reset |
Example
|
G2100# udld reset G2100# |